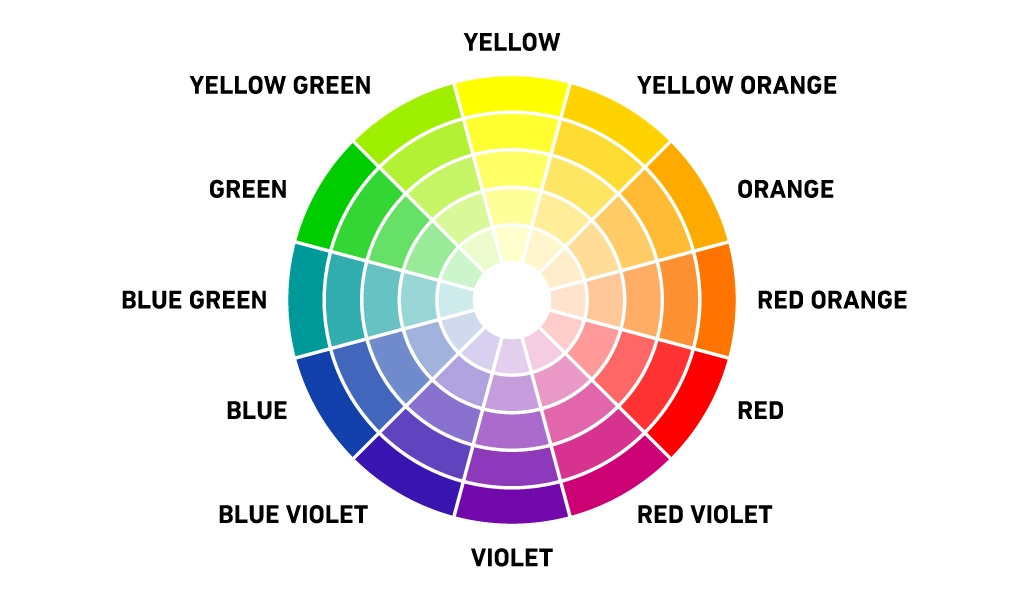
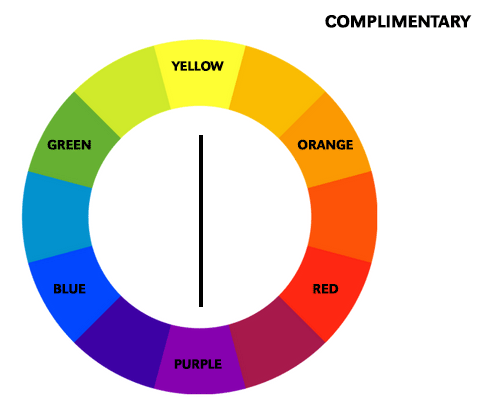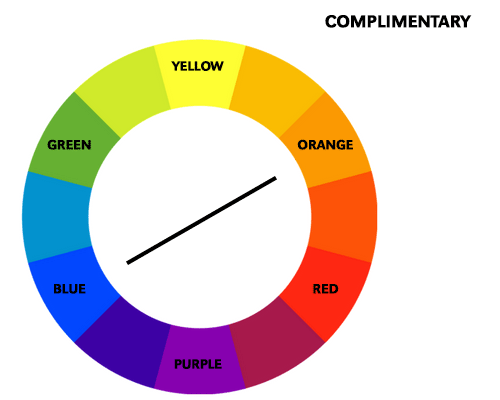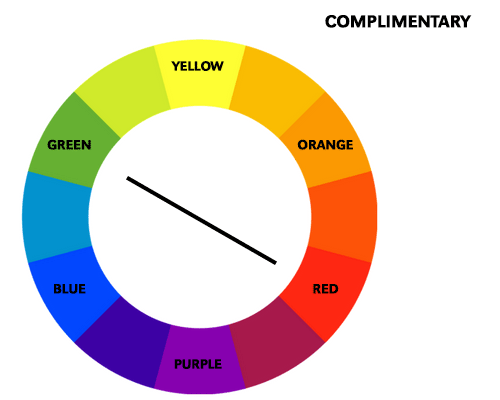
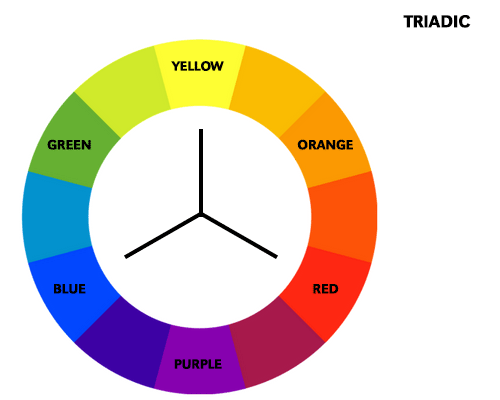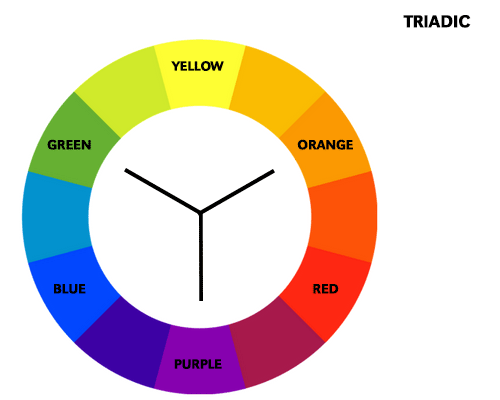
Color schemes are predefined combinations of colors that are used in art and design to create different effects. There are four main types of color schemes:
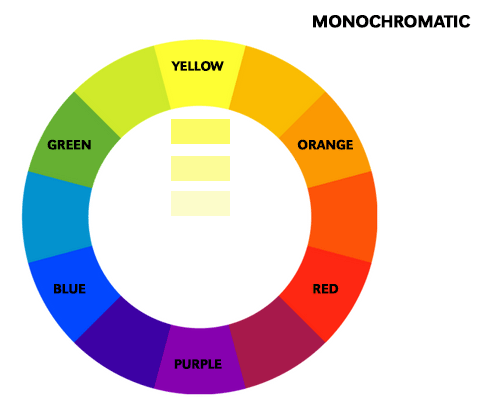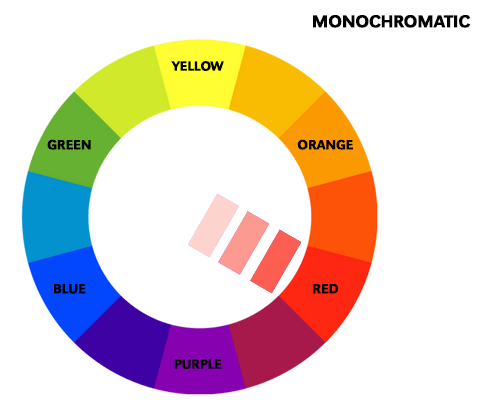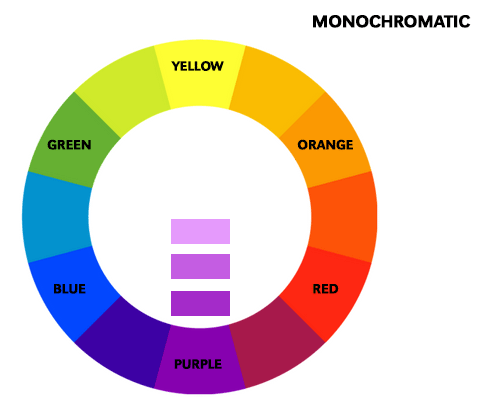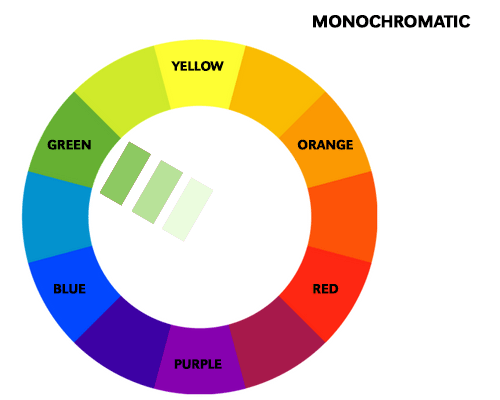
A monochromatic color scheme is based on a single color and its variations in shades, tints, and tones. This scheme is often used for creating a calm and peaceful atmosphere. For example, a painting with different shades of blue can evoke a sense of serenity and tranquility. A monochromatic scheme is also effective in creating depth and dimension in an artwork.
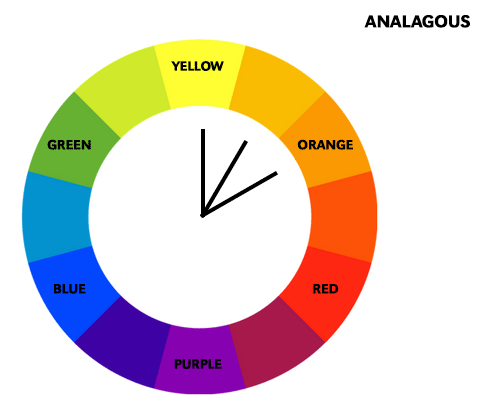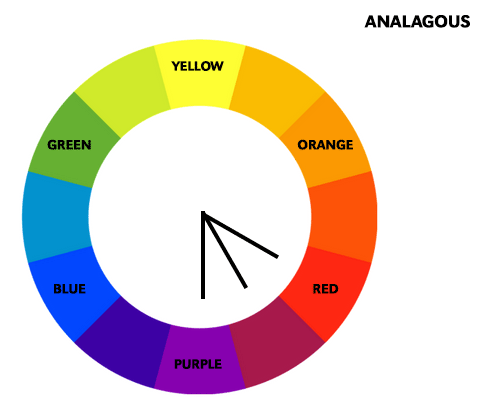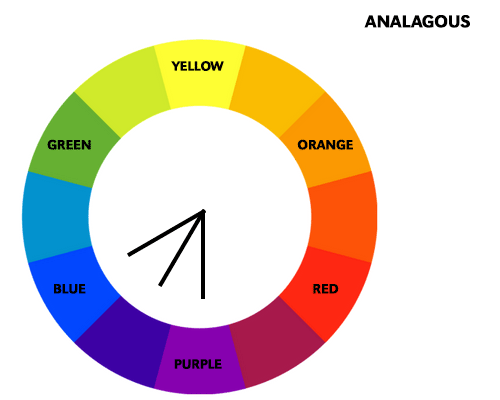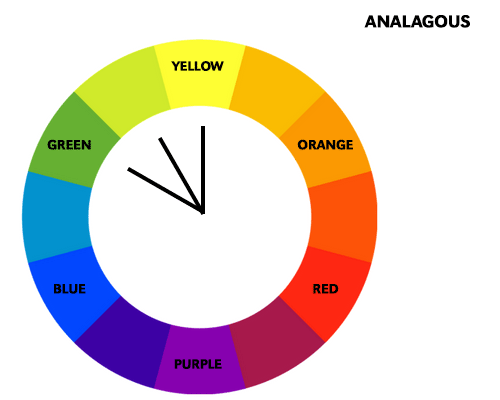
An analogous color scheme is made up of colors that are adjacent to each other on the color wheel, such as red, orange, and yellow. This scheme is often used for creating a natural and cohesive look. For example, a landscape painting with green, yellow, and orange can create a sense of harmony and balance. An analogous scheme can also be used to create a gradient effect, where one color gradually transitions into another.
A complementary color scheme is based on colors that are opposite to each other on the color wheel, such as blue and orange, or red and green. This scheme creates a high contrast and dynamic effect. For example, a painting with red and green can create a sense of tension and energy. A complementary scheme can also be used to highlight certain elements in an artwork.
A triadic color scheme is made up of three colors that are evenly spaced on the color wheel, such as red, yellow, and blue. This scheme creates a vibrant and balanced effect. For example, a painting with red, yellow, and blue can create a sense of excitement and energy. A triadic scheme can also be used to create a variety of contrasts and harmonies in an artwork.