In this lesson, you will learn about testing and validation. Testing ensures your app works as expected, while validation checks that inputs are correct and safe. You will create a simple Flask app with a form to add users to a database, test it manually, and add validation to handle invalid data.
In this lesson, you will learn about testing and validation. Testing ensures your app works as expected, while validation checks that inputs are correct and safe. You will create a simple Flask app with a form to add users to a database, test it manually, and add validation to handle invalid data.
By the end, you will know how to perform basic tests, validate user inputs, and ensure your app handles errors gracefully.
First, create a new folder for this lesson's project and set up the environment.
FlaskTesting'.File > Open Folder).Next, create a virtual environment.
View > Command Palette.Python: Create Environment' and select it.Venv'.Python version..venv' folder.Open a terminal in VS Code to install Flask.
View > Terminal.pip install flask.Create a sample SQLite database with a 'users' table for this lesson.
Create a new file called 'create_db.py' in your project folder and add the following code:
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('users.db')
c = conn.cursor()
# Create table with CHECK constraint to enforce integer type for age
c.execute('''CREATE TABLE users
(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
age INTEGER NOT NULL CHECK (typeof(age) = 'integer'))''')
# Insert sample data
c.execute("INSERT INTO users (name, age) VALUES ('Alice', 25)")
c.execute("INSERT INTO users (name, age) VALUES ('Bob', 30)")
conn.commit()
conn.close()
print('Database created successfully!')Run this script in the terminal: python create_db.py.
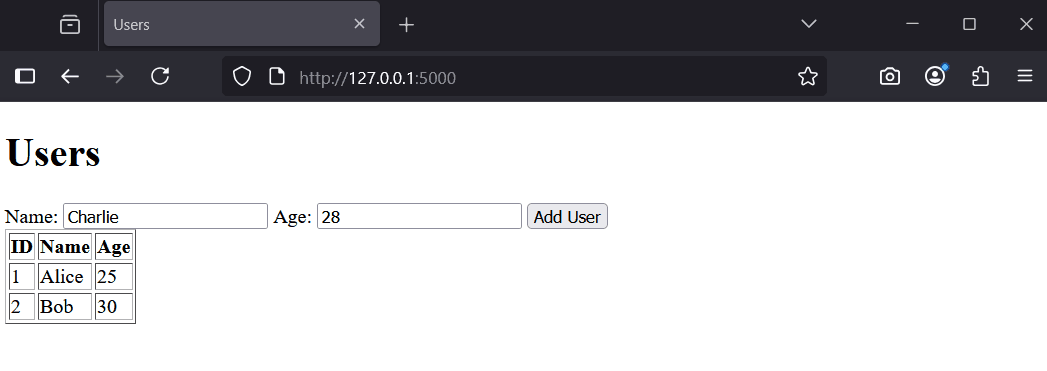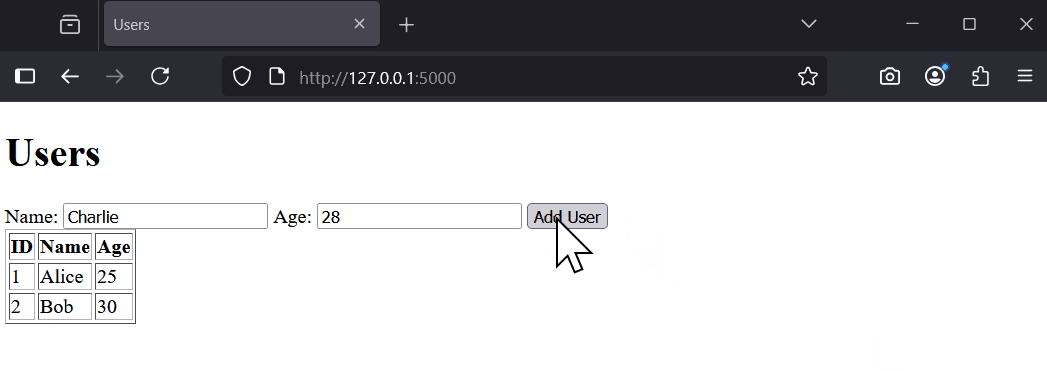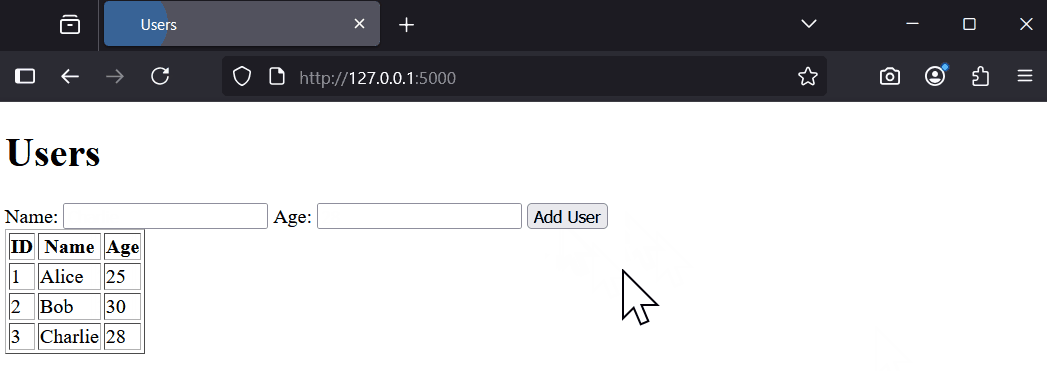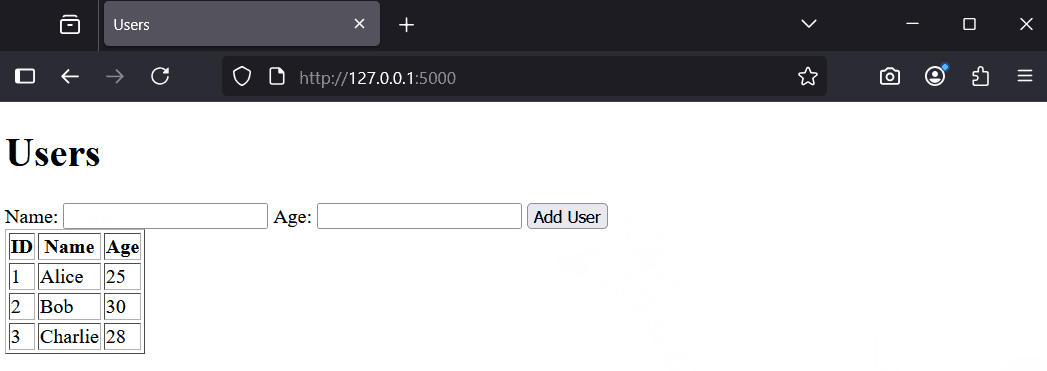
You should see 'Database created successfully!' and a new file 'users.db' in your folder. This database has a users table with two sample records.
Now, create a basic Flask app with a form to add users and display them. This will be the base for testing and validation.
Create a file called 'app.py' and add the following code:
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, redirect
import sqlite3
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def home():
if request.method == 'POST':
name = request.form['name']
age = request.form['age']
conn = sqlite3.connect('users.db')
c = conn.cursor()
c.execute("INSERT INTO users (name, age) VALUES (?, ?)", (name, age))
conn.commit()
conn.close()
return redirect('/')
conn = sqlite3.connect('users.db')
c = conn.cursor()
c.execute("SELECT * FROM users")
users = c.fetchall()
conn.close()
return render_template('users.html', users=users)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)Create a 'templates' folder, then create 'users.html' inside it with:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>Users</title></head>
<body>
<h1>Users</h1>
<form method="post">
<label>Name: <input type="text" name="name"></label>
<label>Age: <input type="text" name="age"></label>
<button type="submit">Add User</button>
</form>
<table border="1">
<tr><th>ID</th><th>Name</th><th>Age</th></tr>
{% for user in users %}
<tr><td>{{ user[0] }}</td><td>{{ user[1] }}</td><td>{{ user[2] }}</td></tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</body>
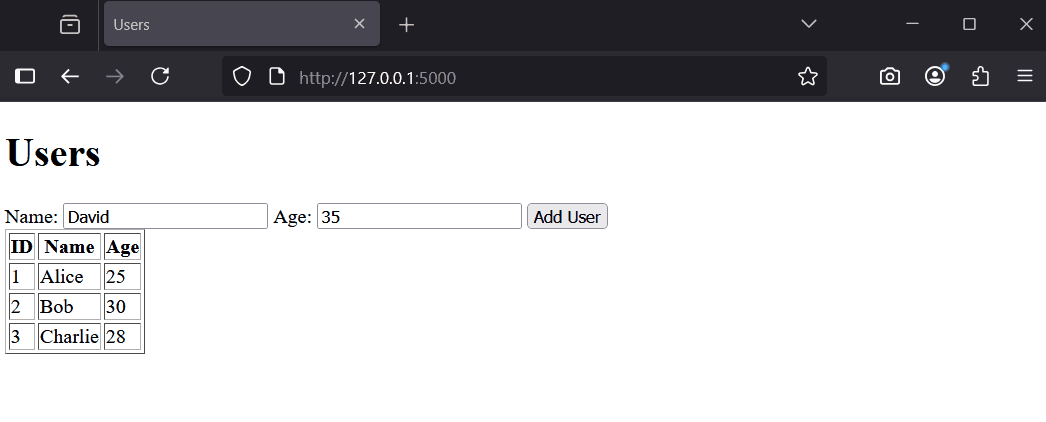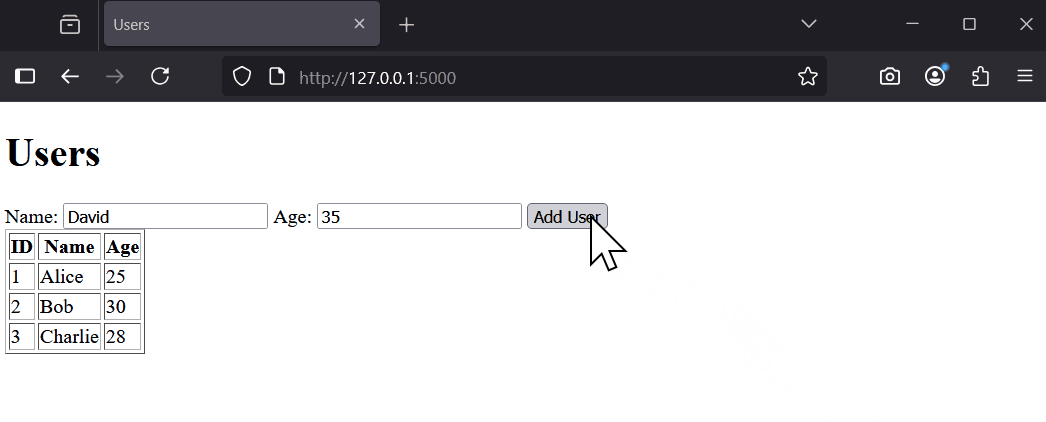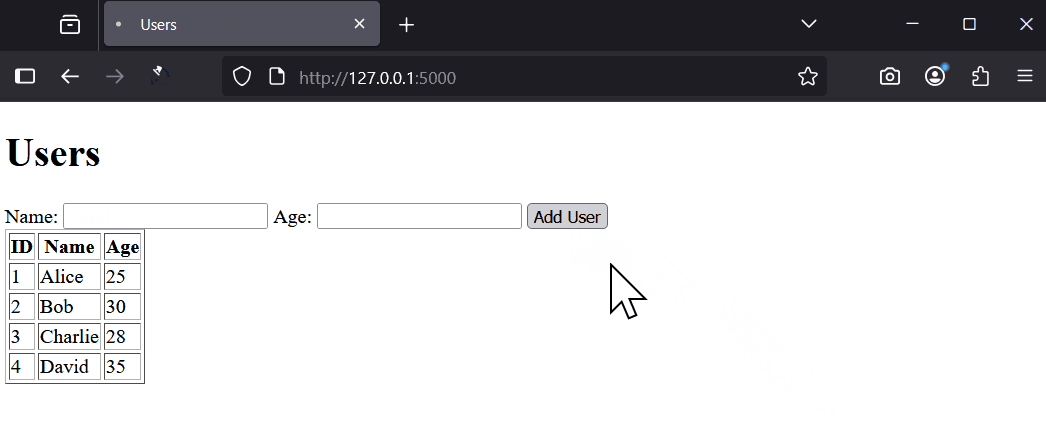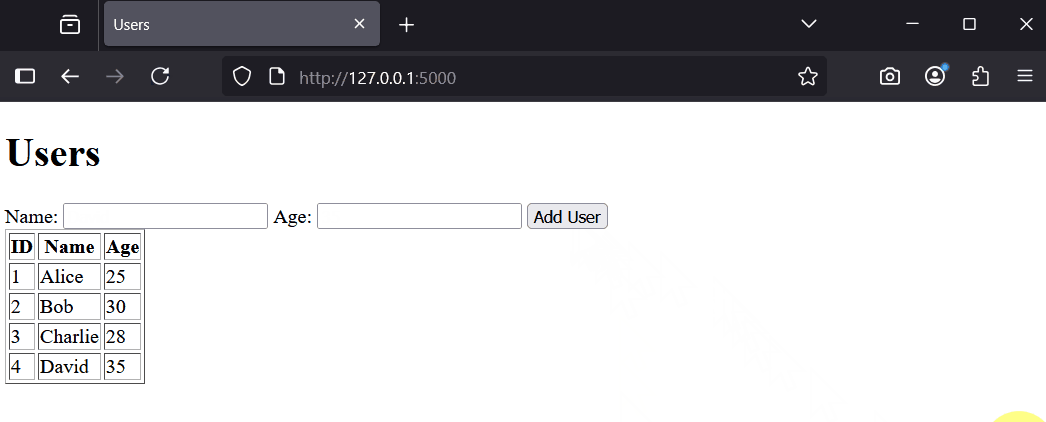
</html>Run the app: python app.py. Visit http://127.0.0.1:5000/ to see the form and users list.
Try adding a user, like 'Charlie' with age 28. Refresh to see the updated list.
Testing means checking if your app works as expected. We will do manual tests without automated tools.
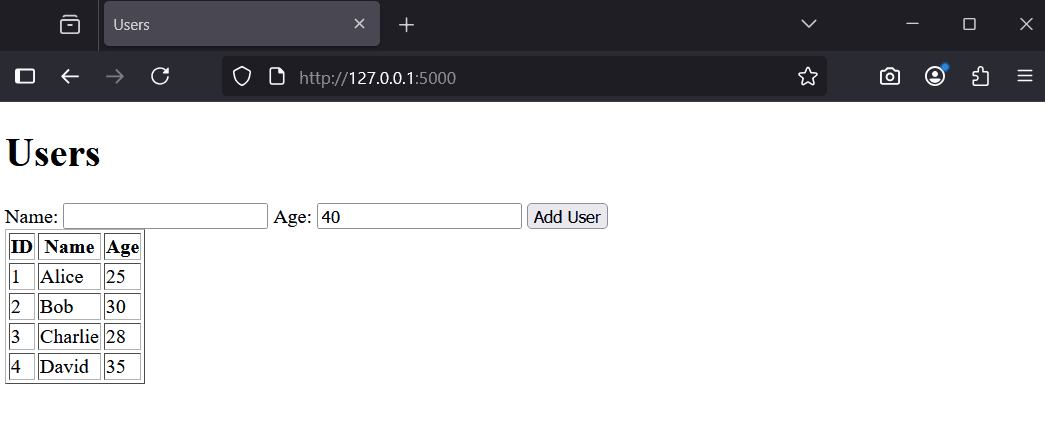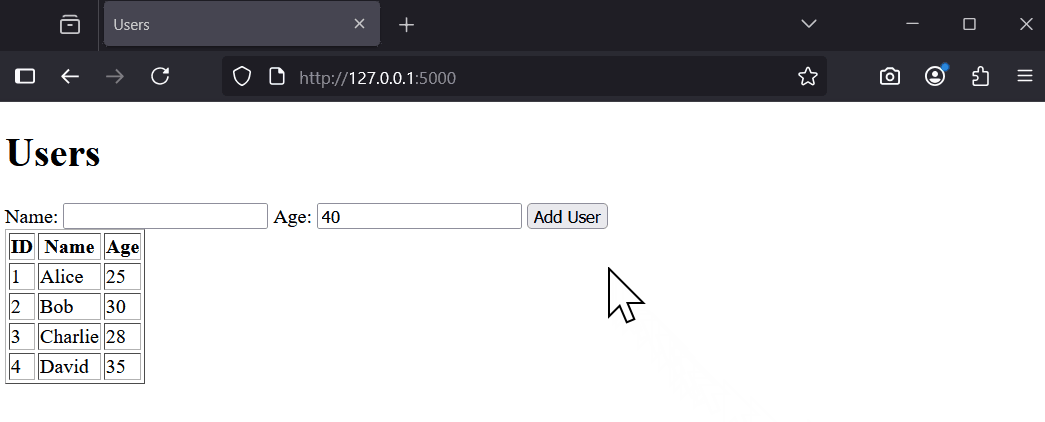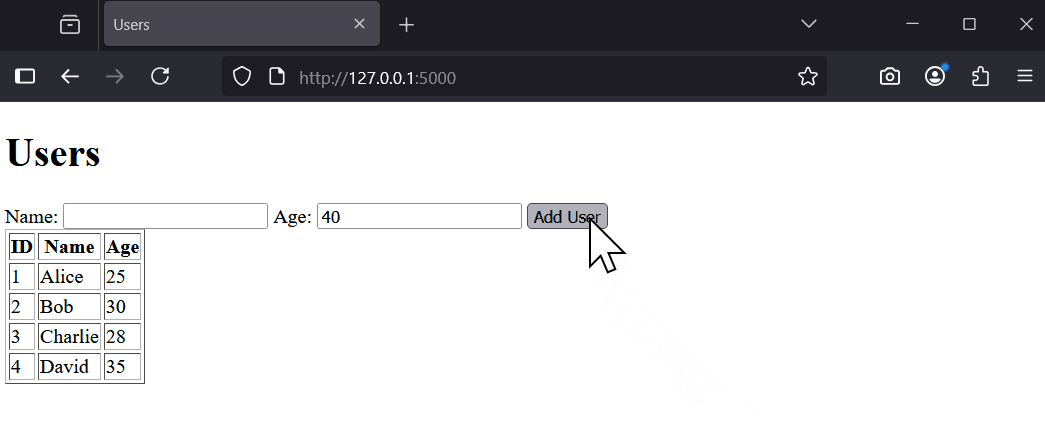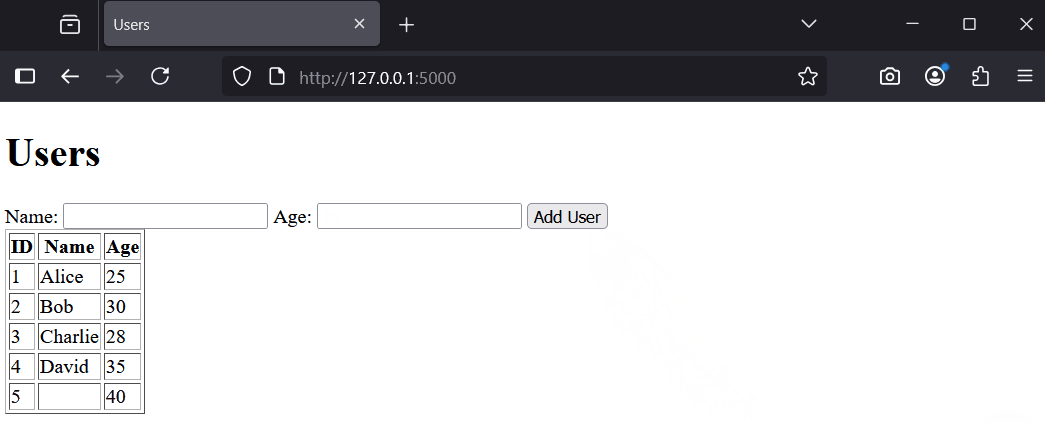
With your app running, perform these tests:
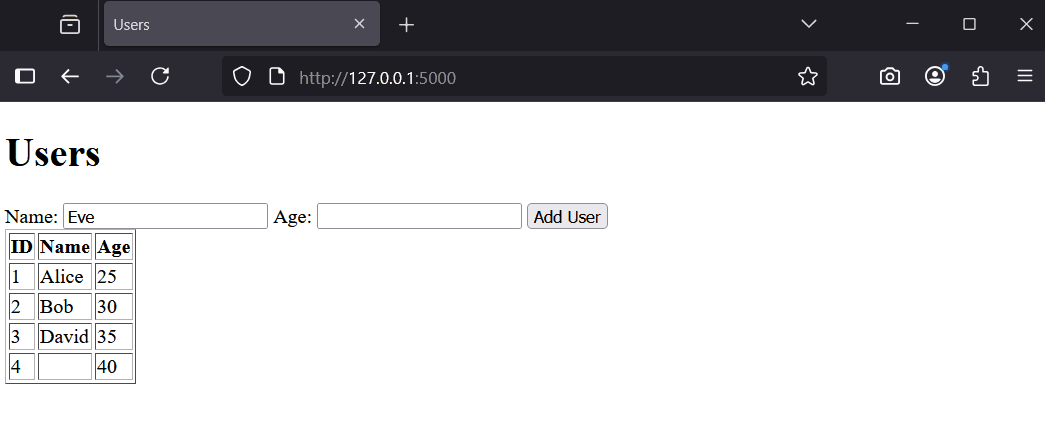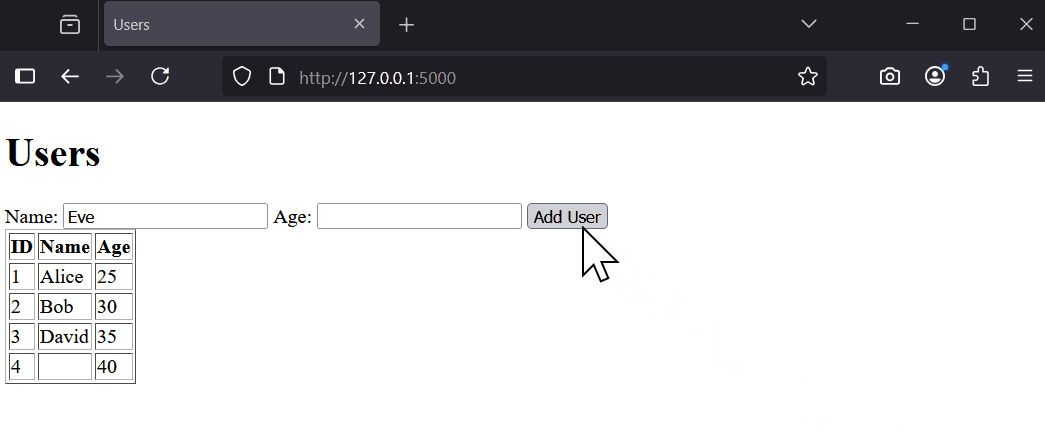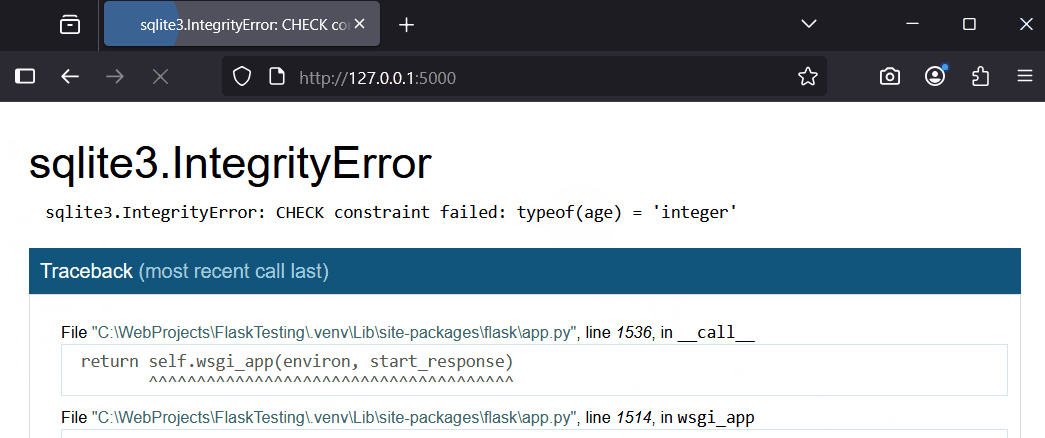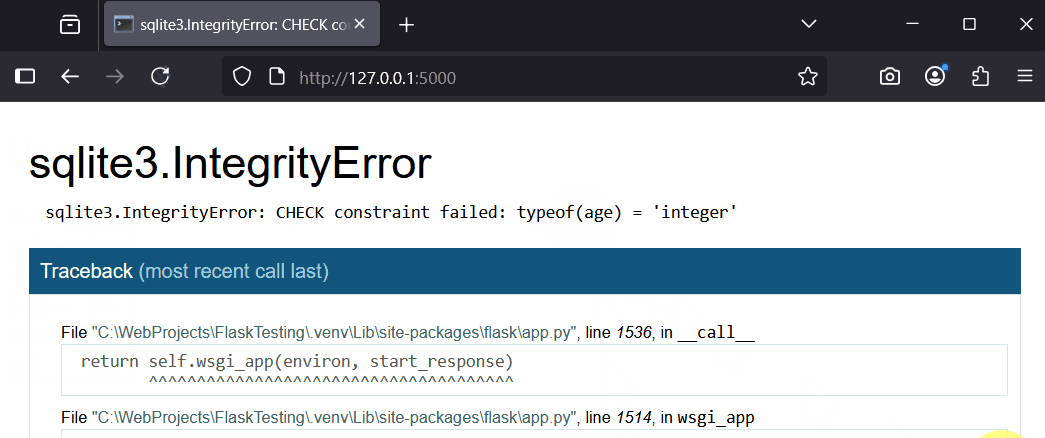
These tests reveal issues like accepting invalid data or crashing on errors. Next, we will add validation to fix this.