If we look at the following sum: 7 + 4 = 11
The + is the operator and the 7 and the 4 are the operands.
So the numbers are called operands and the operation (to be performed between the two operands) is defined by an operator.
In JavaScript we can use the following types of operators.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Arithmetic Operators |
For adding, subtracting, multiplication and division. |
| String Operators | For joining strings together. |
| Assignment Operators | For assigning values to variables. |
| Comparison Operators | For comparing two different values (equal to, greater than, less than etc.) |
| Logical Operators | For determining the logic between variables or values (and, or, not). |
Arithmetic operators perform arithmetic on numbers. The main arithmetic operators are:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + |
For adding two numbers together. | |
| - | For subtracting one number from another. | |
| * | For multiplying two numbers together. | |
| / | For dividing one number by another. | |
There are also some other arithmetic operators that we can use:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ++ |
For incrementing a number (increasing it by 1). | |
| -- | For decrementing a number (decreasing it by 1). | |
| % | Modulus operator (%) returns the division remainder. | |
Let's try using the arithmetic operators. Go to the https://makecode.microbit.org website, create a new project and switch from Blocks to JavaScript.
Add the following code examples one by one to your project and see if you get the same result in the simulator.
| Add this code | Result |
|---|---|
|
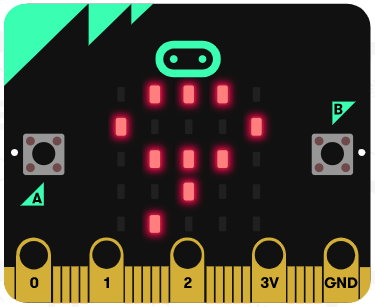 |
|
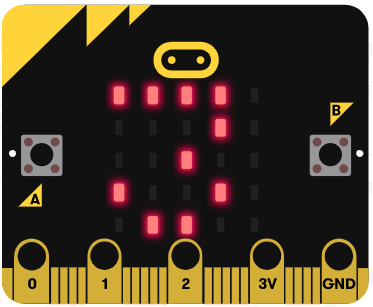 |
|
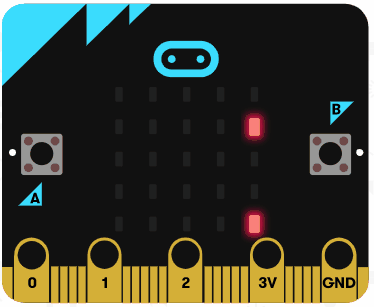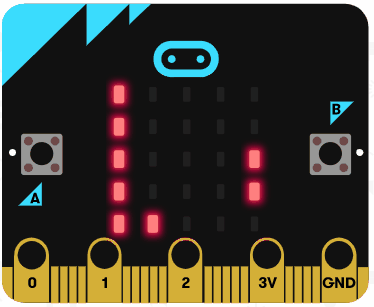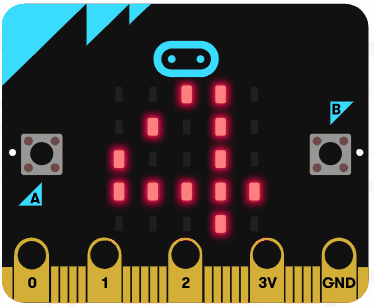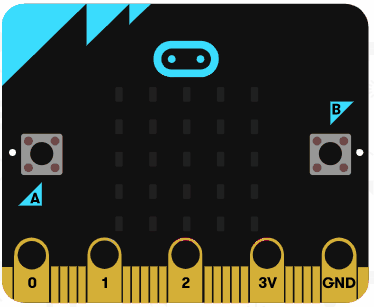 |
|
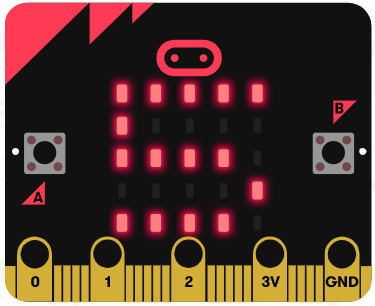 |
|
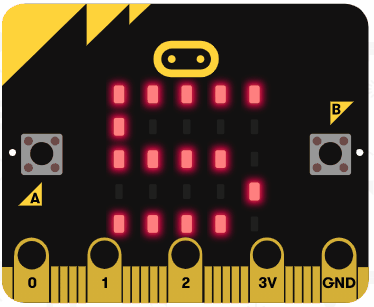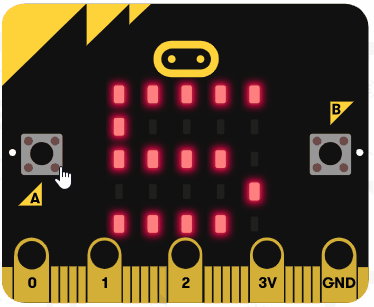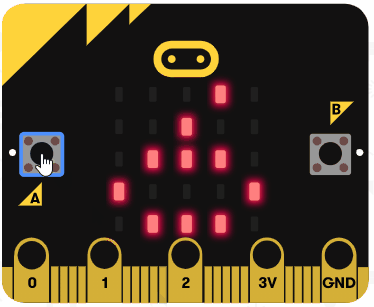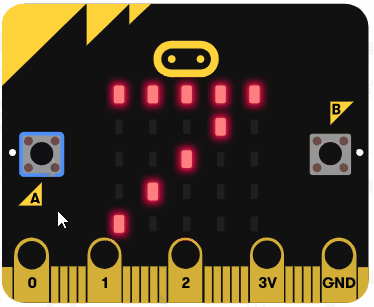 |
|
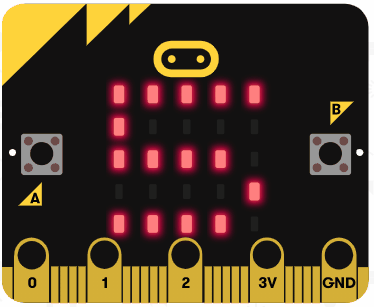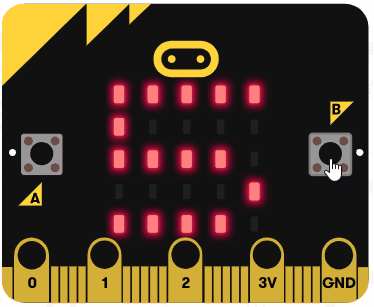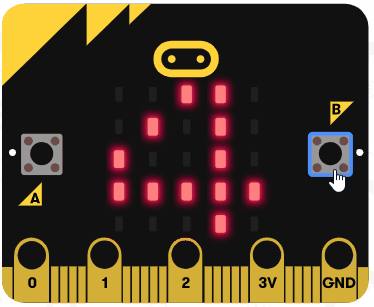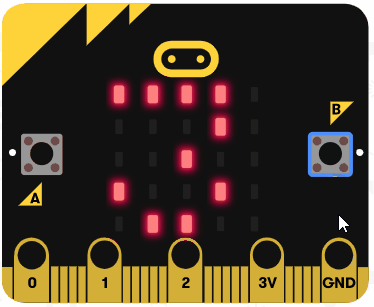 |
The + operator can also be used to join (concatenate) strings together.
let firstName = "Stefan"
let lastName = "Jones"
let fullName = firstName + " " + lastName
This will make fullName equal to Stefan Jones.
If you add strings and numbers together then JavaScript will treat the number as a string.
let fname = "Jane"
let age = 25
let x = fname + age
This will make x equal to Jane25.
Let's try using the string operators. Delete all the previous code that you added.
Add the following code examples one by one to your project and see if you get the same result in the simulator.
| Add this code | Result |
|---|---|
|
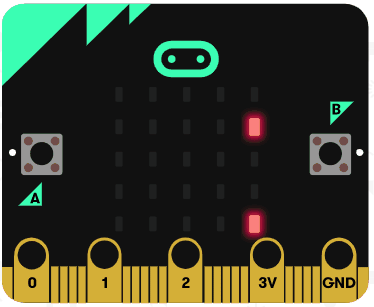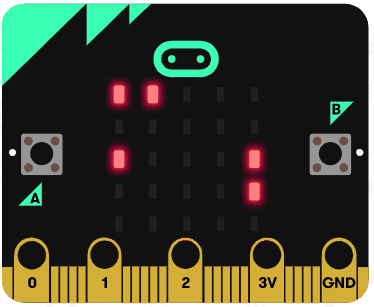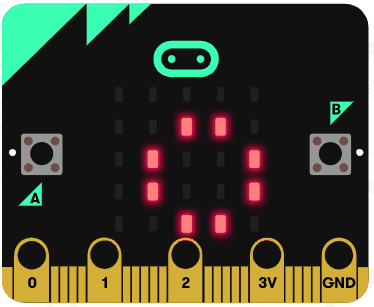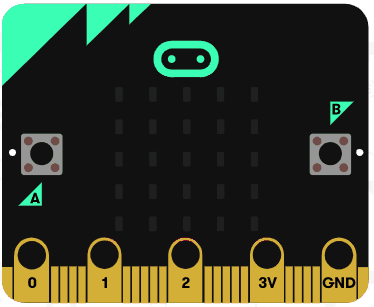 |
|
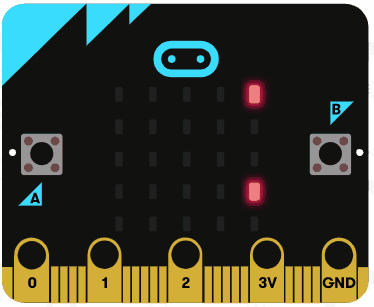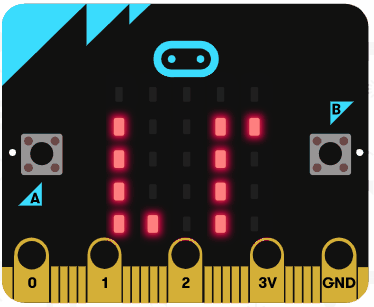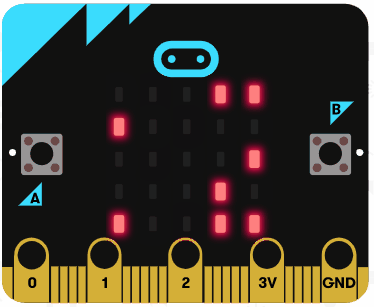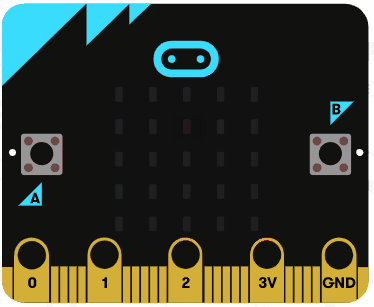 |