Computer Science is the study of computers and how they can be used to solve problems. It involves designing software, understanding algorithms, and exploring how data is processed and stored.
Computer Science is the study of computers and how they can be used to solve problems. It involves designing software, understanding algorithms, and exploring how data is processed and stored.
For example, in modern life, Computer Science is used in various applications such as:
In this course, you'll learn foundational concepts that apply to many fields, from programming to artificial intelligence, helping you develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
 Careers in Computer Science are exciting and varied, with high demand in today's digital world. You could pursue roles such as:
Careers in Computer Science are exciting and varied, with high demand in today's digital world. You could pursue roles such as:
Other options include web development, game design, or even roles in research and innovation. These careers allow you to contribute to solving real-world problems.
A computer system is a combination of hardware and software that work together to process data and perform tasks. In this step, we'll explore these components in more detail to help you understand how computers function in daily life.
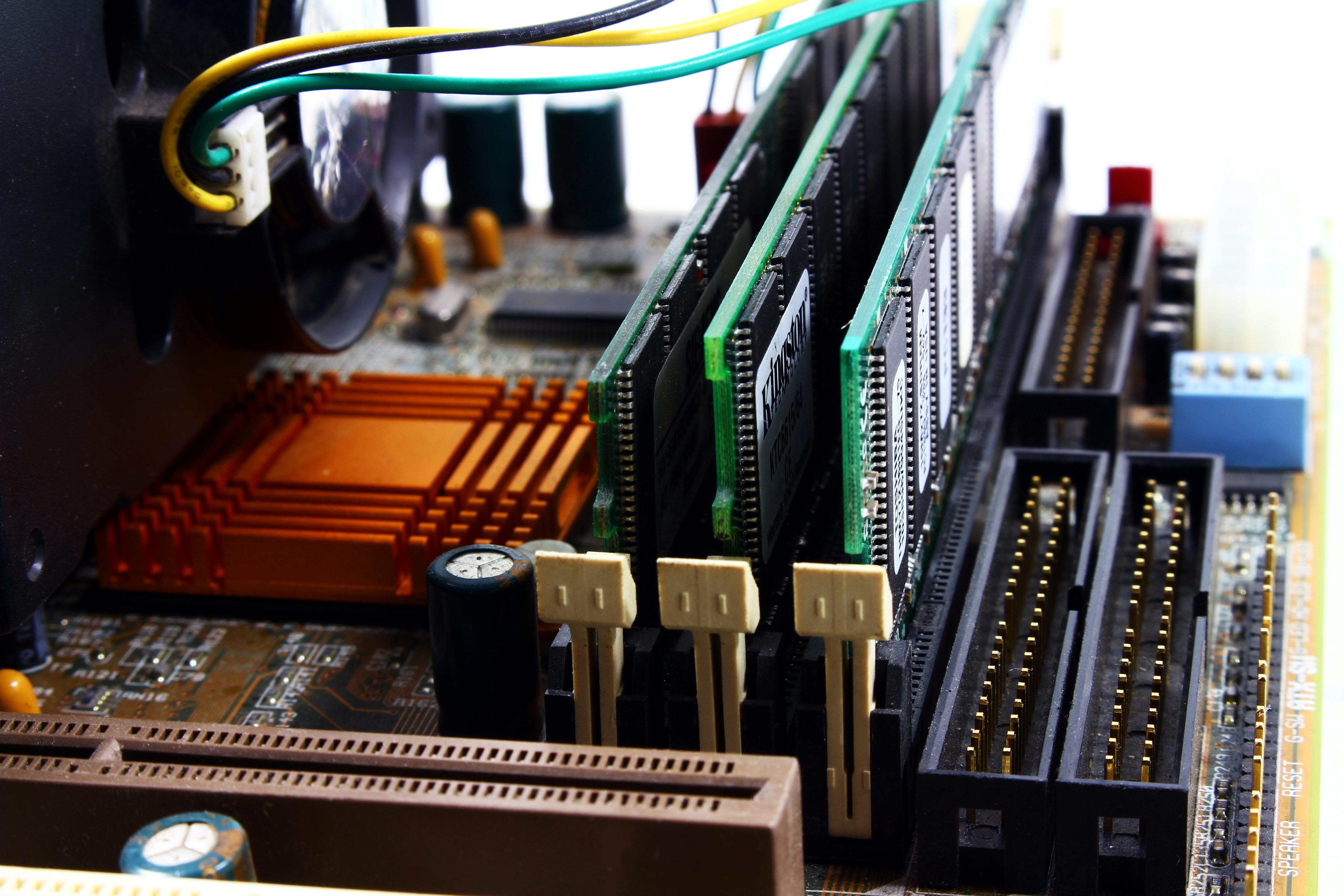 Hardware includes all the tangible components of a computer. These are the parts you can see and touch. The main hardware elements are:
Hardware includes all the tangible components of a computer. These are the parts you can see and touch. The main hardware elements are:
Other hardware might include input devices (e.g., keyboards and mice) and output devices (e.g., screens and speakers), but we'll focus on the core parts here.
 Software is the set of programs and instructions that tell the hardware what to do. It includes operating systems (like Windows or macOS), applications (such as web browsers), and the code we write in code editors. Software acts as a bridge, controlling the hardware and enabling us to interact with the computer effectively.
Software is the set of programs and instructions that tell the hardware what to do. It includes operating systems (like Windows or macOS), applications (such as web browsers), and the code we write in code editors. Software acts as a bridge, controlling the hardware and enabling us to interact with the computer effectively.
By understanding these building blocks, you'll gain insight into how computers handle everything from playing games to managing data in large systems. This knowledge is foundational for exploring more advanced topics in computer science.
Lets introduce you to the BBC micro:bit and the MakeCode editor, which we'll use throughout this module to learn about computer systems through practical coding.
The BBC micro:bit is a small, programmable device that helps you learn about computing. It's like a tiny computer that you can code to do various things, such as displaying messages on its LED screen or reacting to buttons. Even if you don't have a physical micro:bit, you can use the virtual simulator in the editor.
The MakeCode editor is an online tool where you can write code using blocks, Python or JavaScript to program the micro:bit. You can access it by going to makecode.microbit.org. We'll be using this editor to create block-based code in this first module.
Remember, you don't need a physical micro:bit to follow along; the simulator in the editor works perfectly. If you do have one, you can optionally download your code to it and run the code on the physical device.
Go to the Makecode.com Microbit website using the link below and click on the 'New Project' button underneath the 'My Projects' heading.
https://makecode.microbit.org/
Install the micro:bit app on your iPad or tablet.
Open the app, tap 'Create code' and then create a new project.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is oft en called the 'brain' of a computer system. It is responsible for executing instructions from software programs, performing calculations, and controlling other hardware components to ensure everything works together smoothly. In simple terms, the CPU processes data and runs code, making it possible for computers to perform tasks like browsing the internet or running games.
en called the 'brain' of a computer system. It is responsible for executing instructions from software programs, performing calculations, and controlling other hardware components to ensure everything works together smoothly. In simple terms, the CPU processes data and runs code, making it possible for computers to perform tasks like browsing the internet or running games.
To understand the CPU better, consider its core process known as the fetch-decode-execute cycle. This cycle involves three main steps:
This cycle repeats billions of times per second in modern CPUs, enabling rapid processing and responsiveness in devices.
 CPUs are not limited to computers; they are found in a wide array of everyday technology. For example, in smartphones, the CPU handles multitasking, such as switching between apps, processing images, and managing notifications. In vehicles, CPUs power systems for navigation, engine control, and safety features like adaptive cruise control. Even in household items like smart thermostats or fitness trackers, CPUs process data from sensors to provide real-time feedback and automation. This widespread use demonstrates how CPUs make devices efficient and interactive, responding quickly to user inputs and environmental changes.
CPUs are not limited to computers; they are found in a wide array of everyday technology. For example, in smartphones, the CPU handles multitasking, such as switching between apps, processing images, and managing notifications. In vehicles, CPUs power systems for navigation, engine control, and safety features like adaptive cruise control. Even in household items like smart thermostats or fitness trackers, CPUs process data from sensors to provide real-time feedback and automation. This widespread use demonstrates how CPUs make devices efficient and interactive, responding quickly to user inputs and environmental changes.
By grasping these concepts, you'll build a solid foundation for understanding how computers and other systems operate.
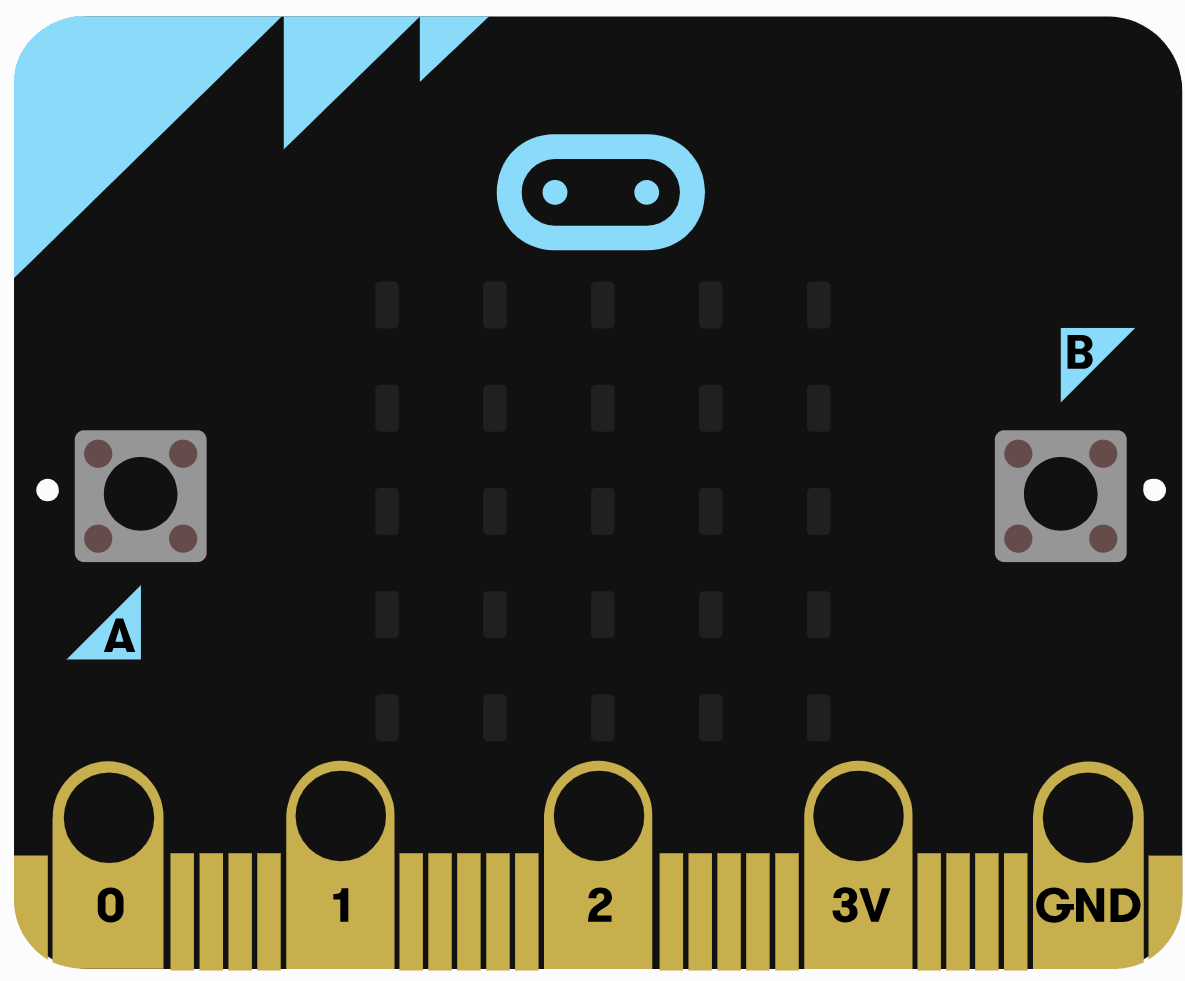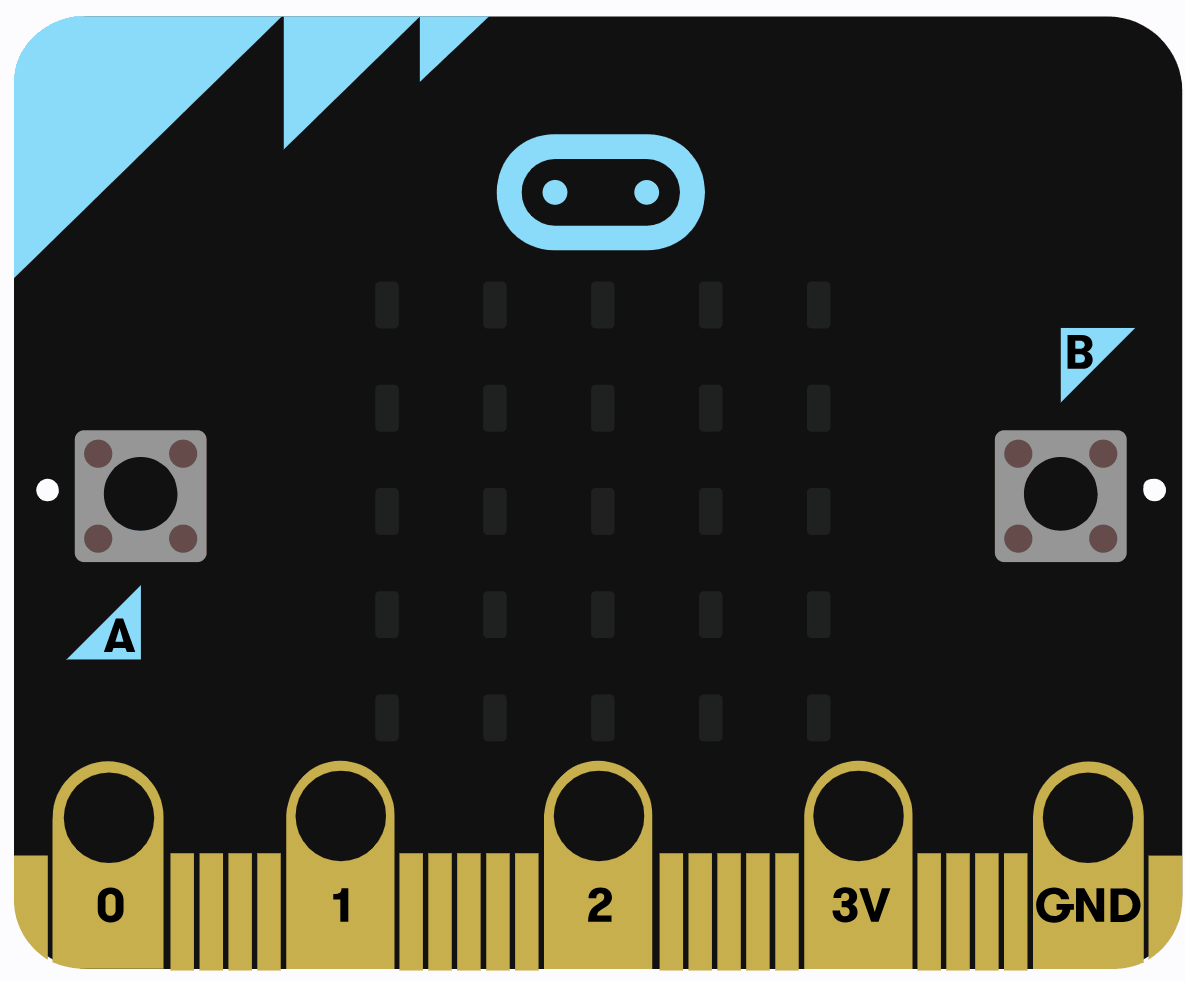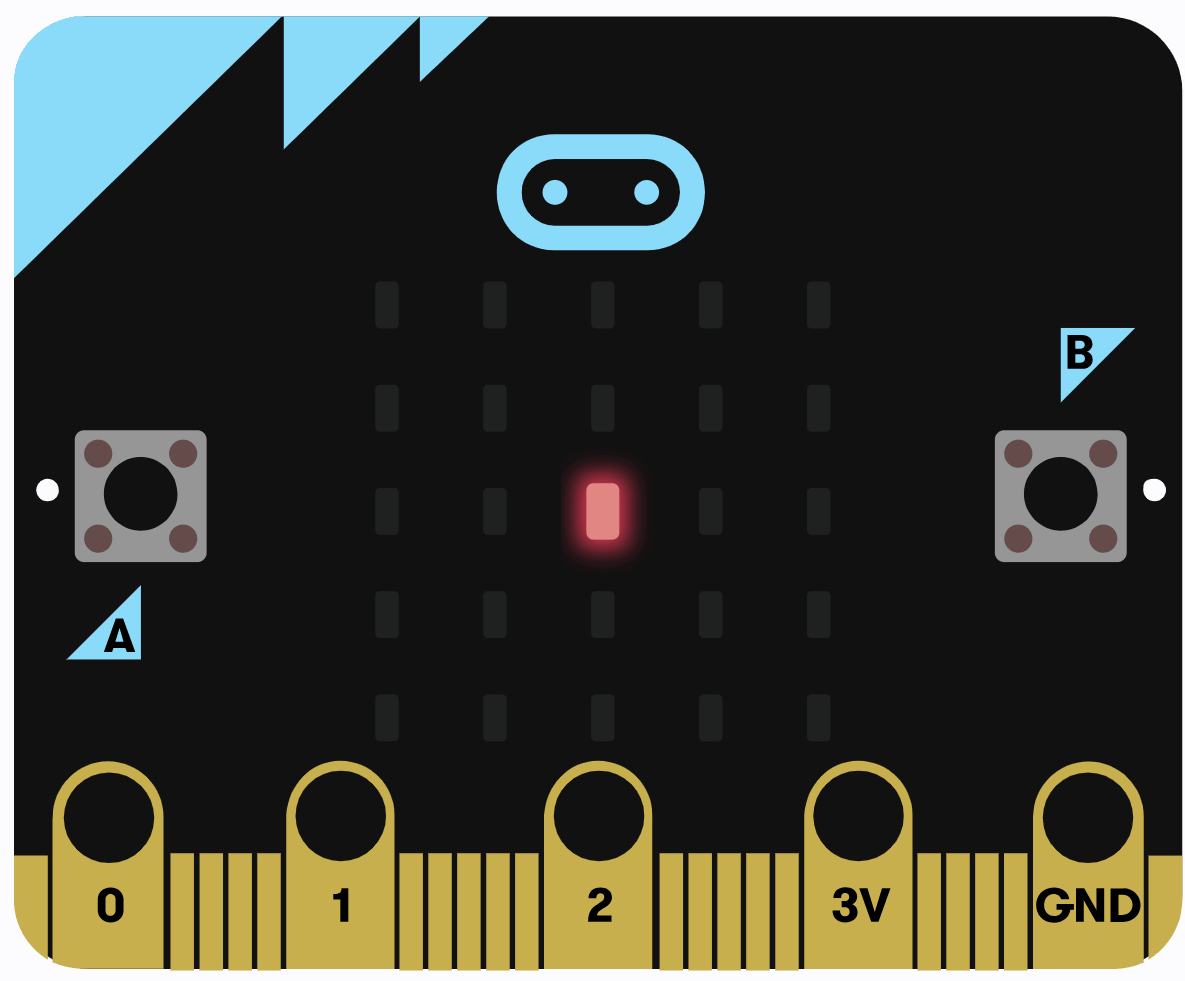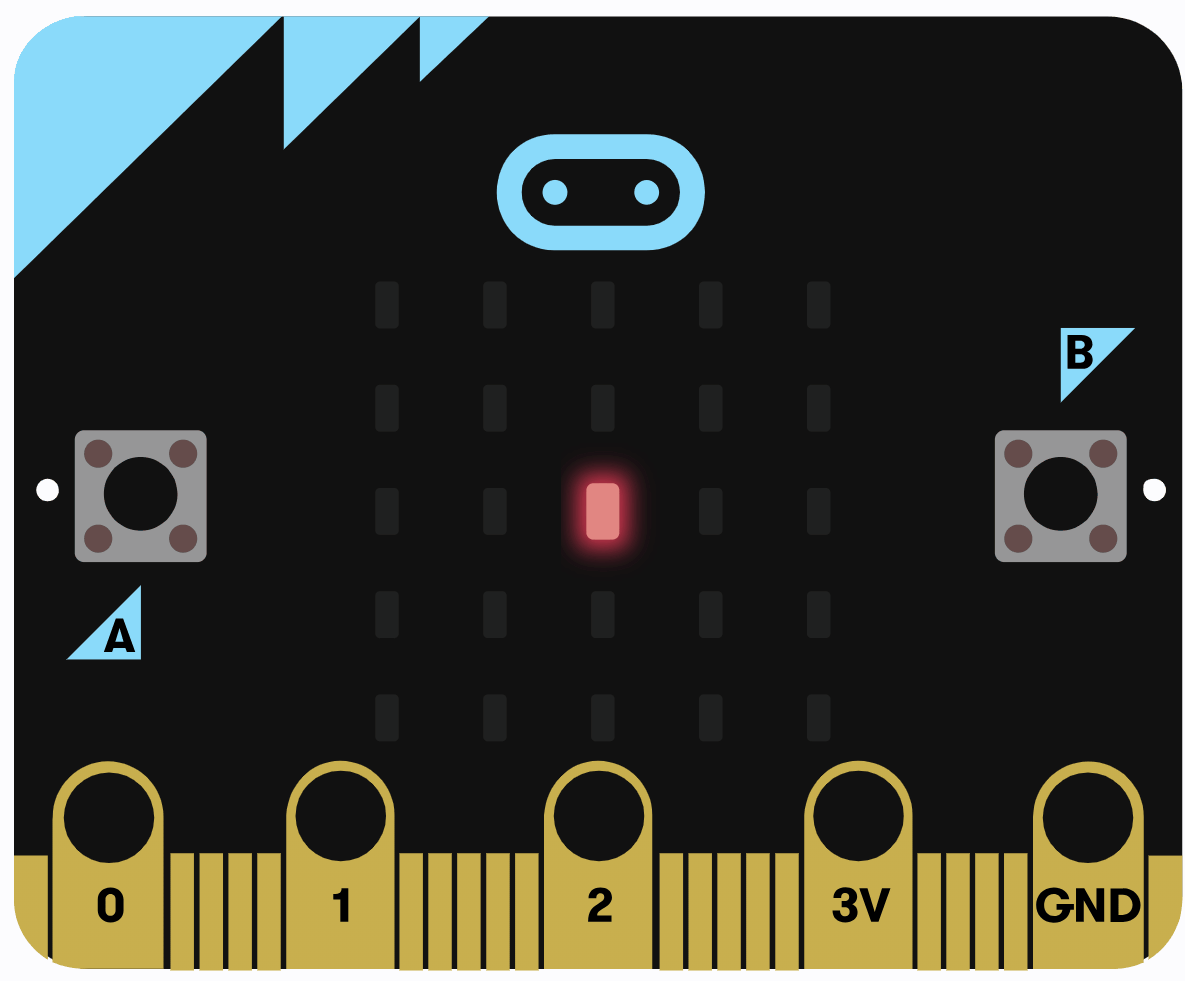
Let's create a simple program that makes an LED blink on and off continuously, demonstrating how the CPU handles repetitive tasks by fetching instructions from memory, decoding them, and executing actions like controlling the LEDs in a loop.
Open the MakeCode editor by going to makecode.microbit.org. We'll use this to write and test your code using the simulator. If you have a physical micro:bit, you can optionally download the code onto the device.
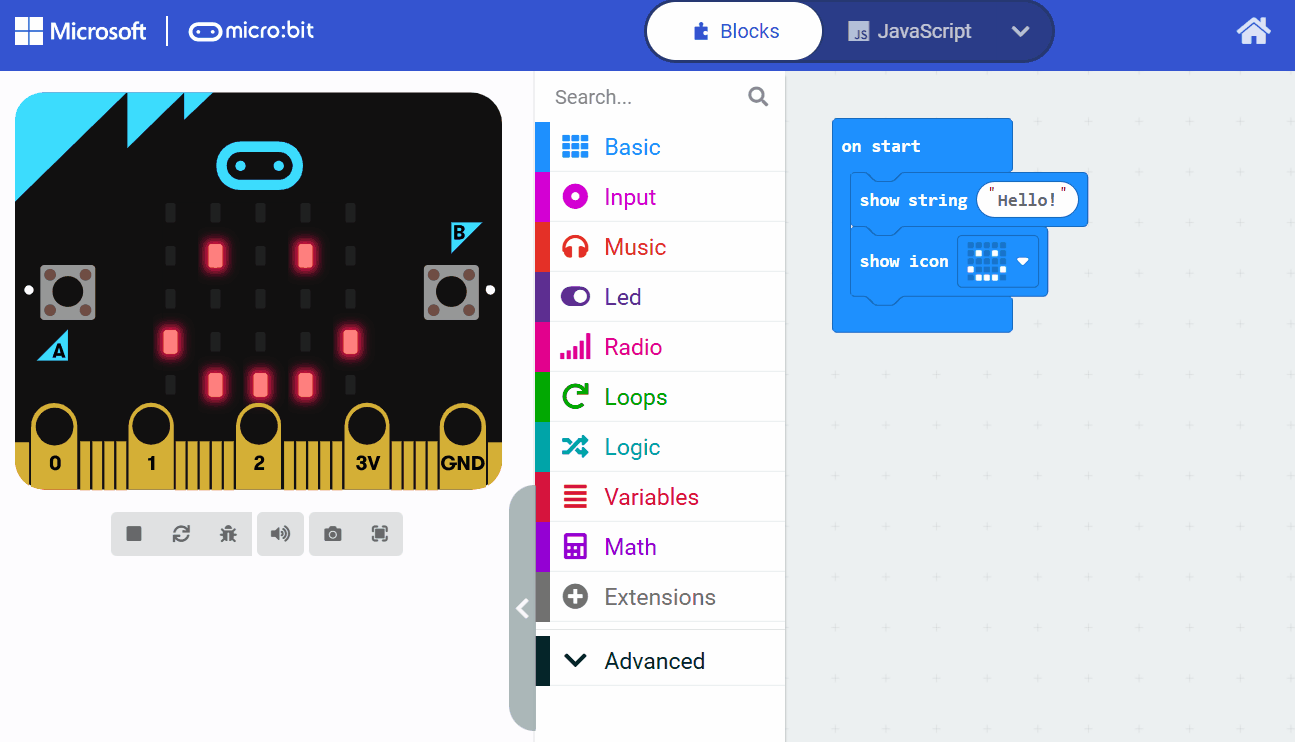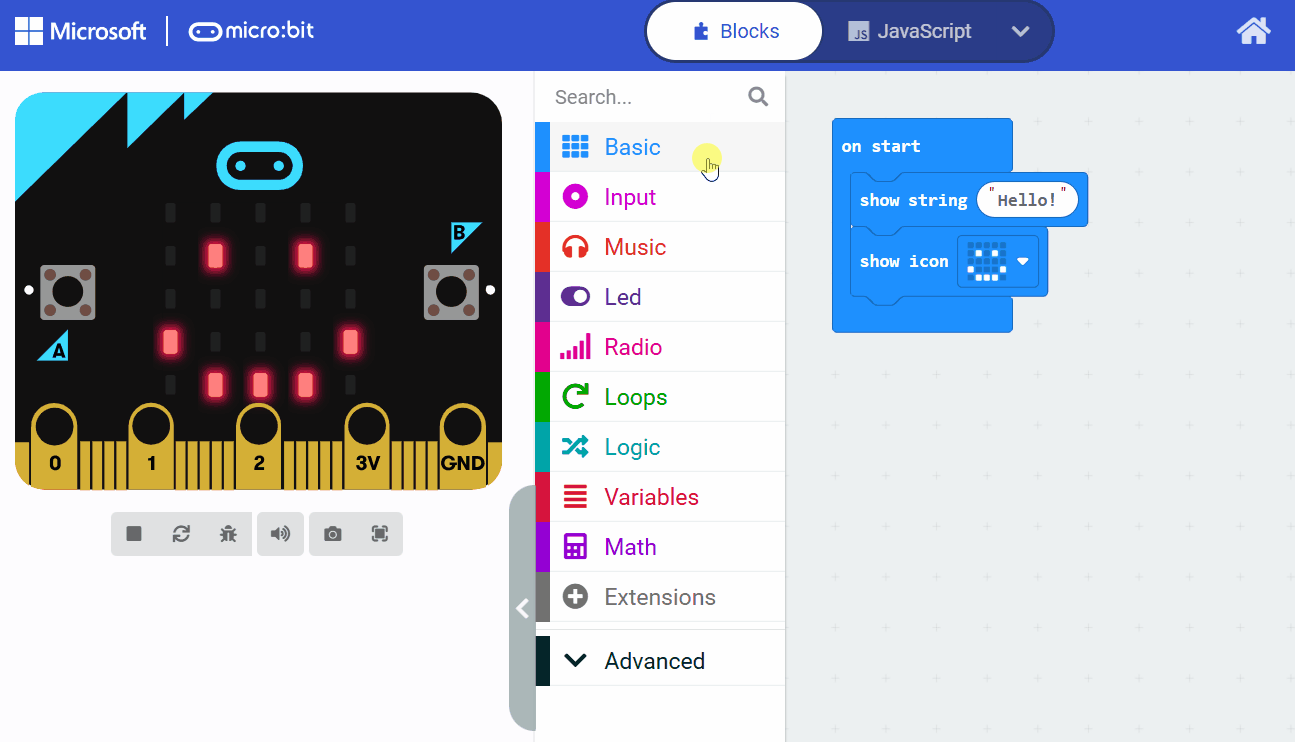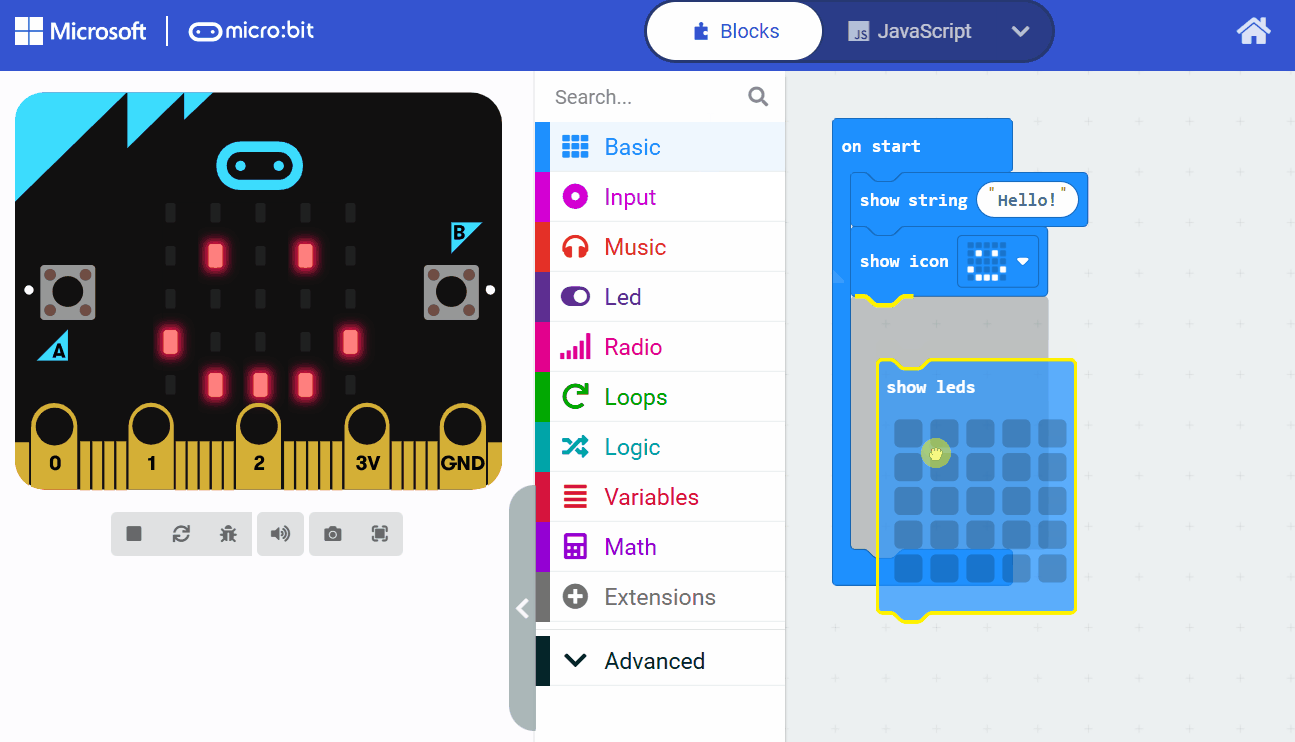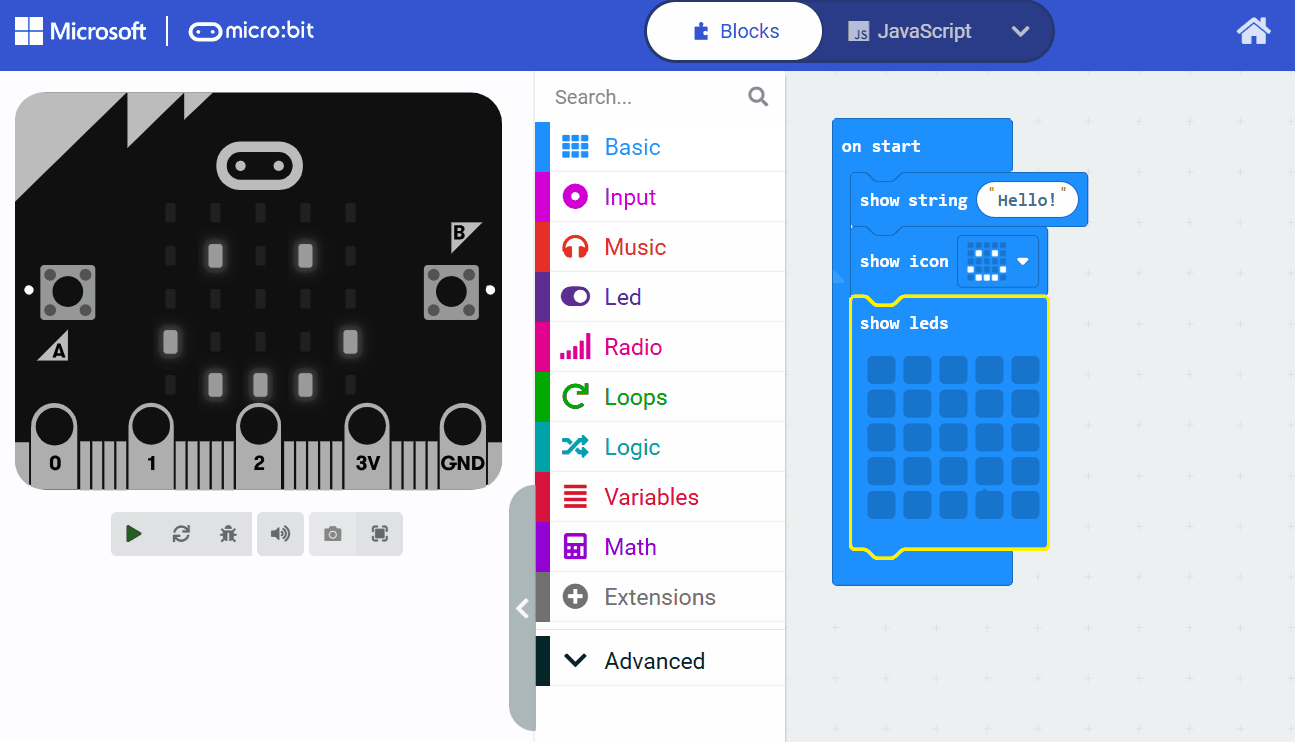
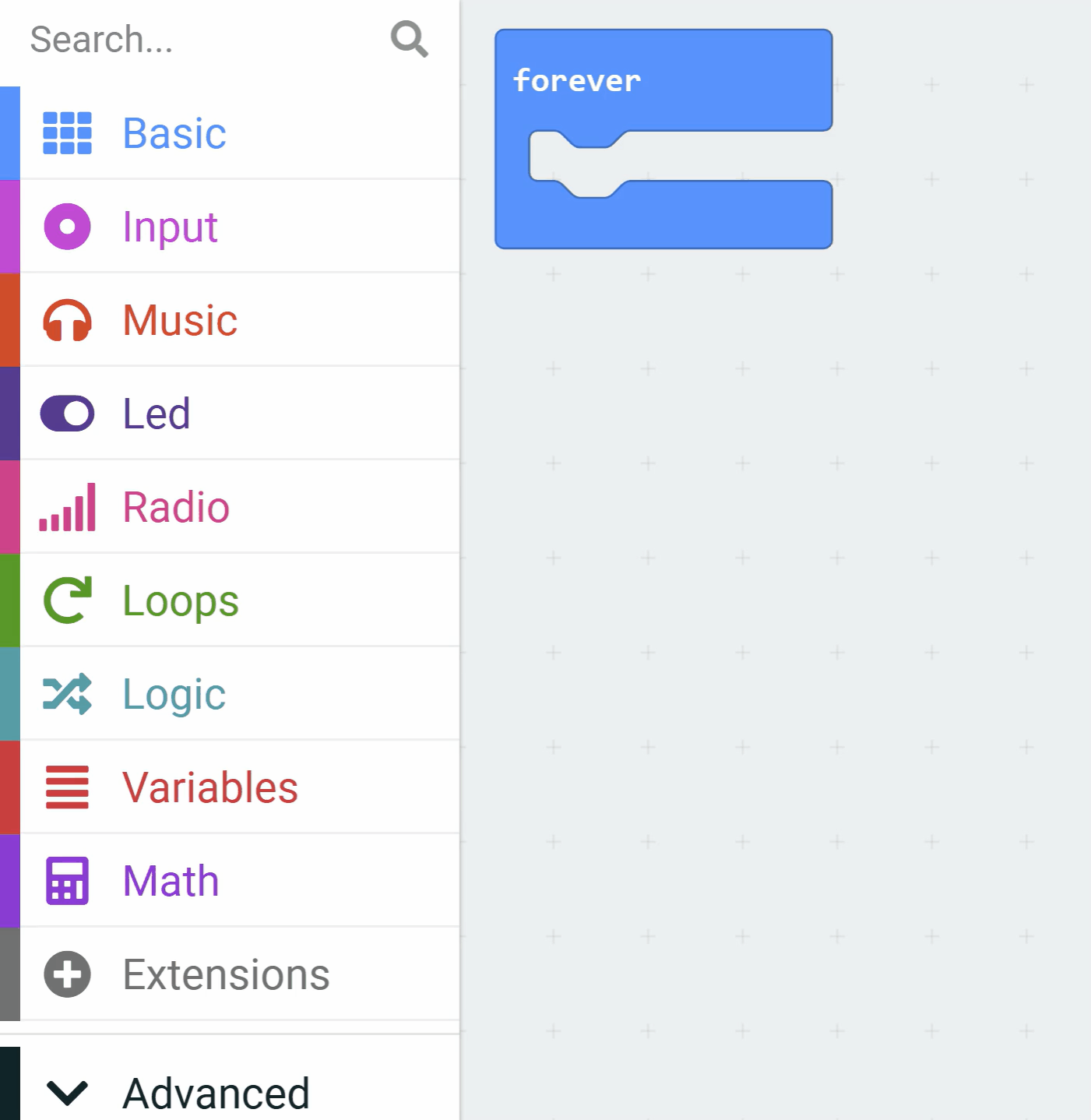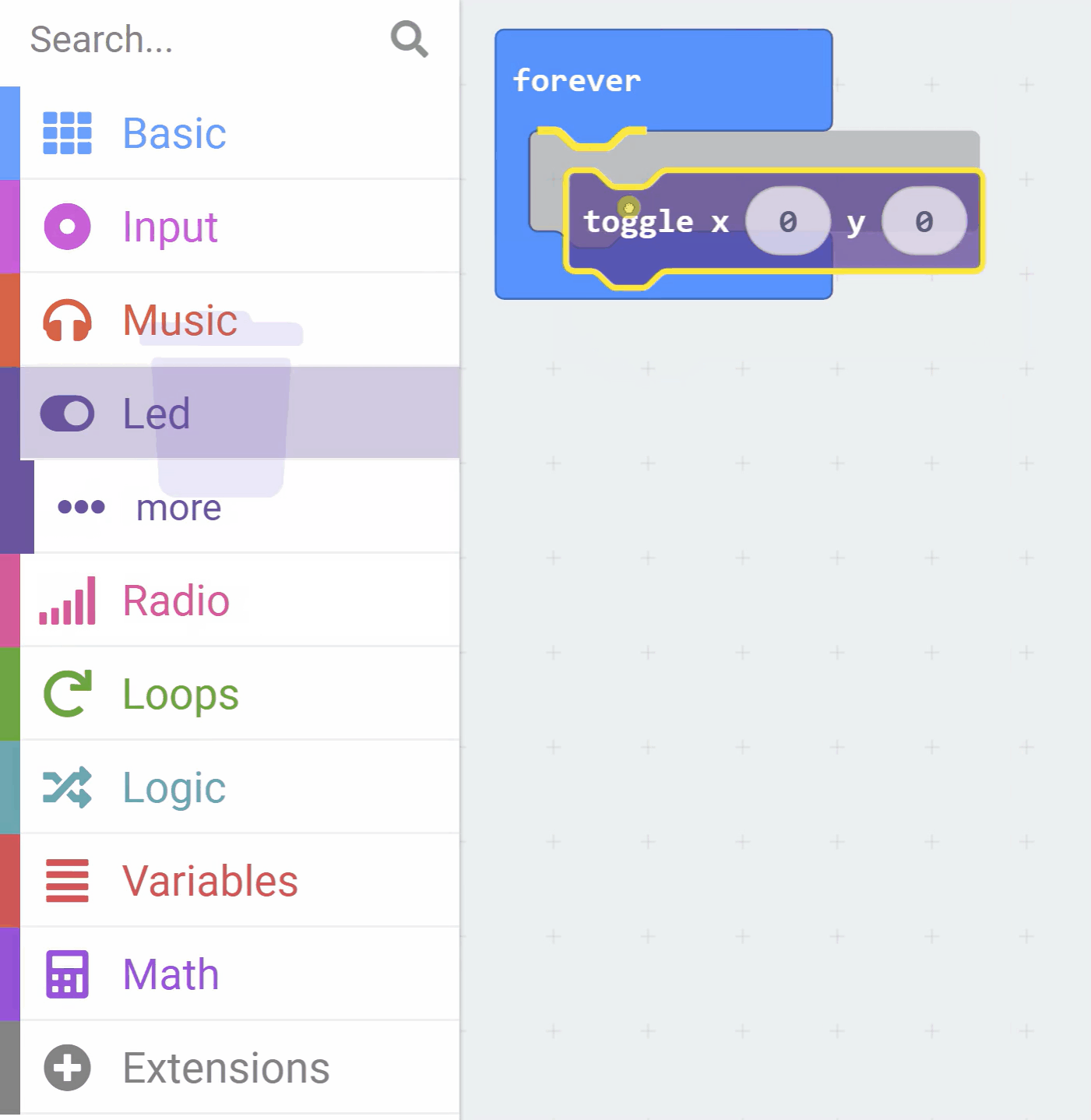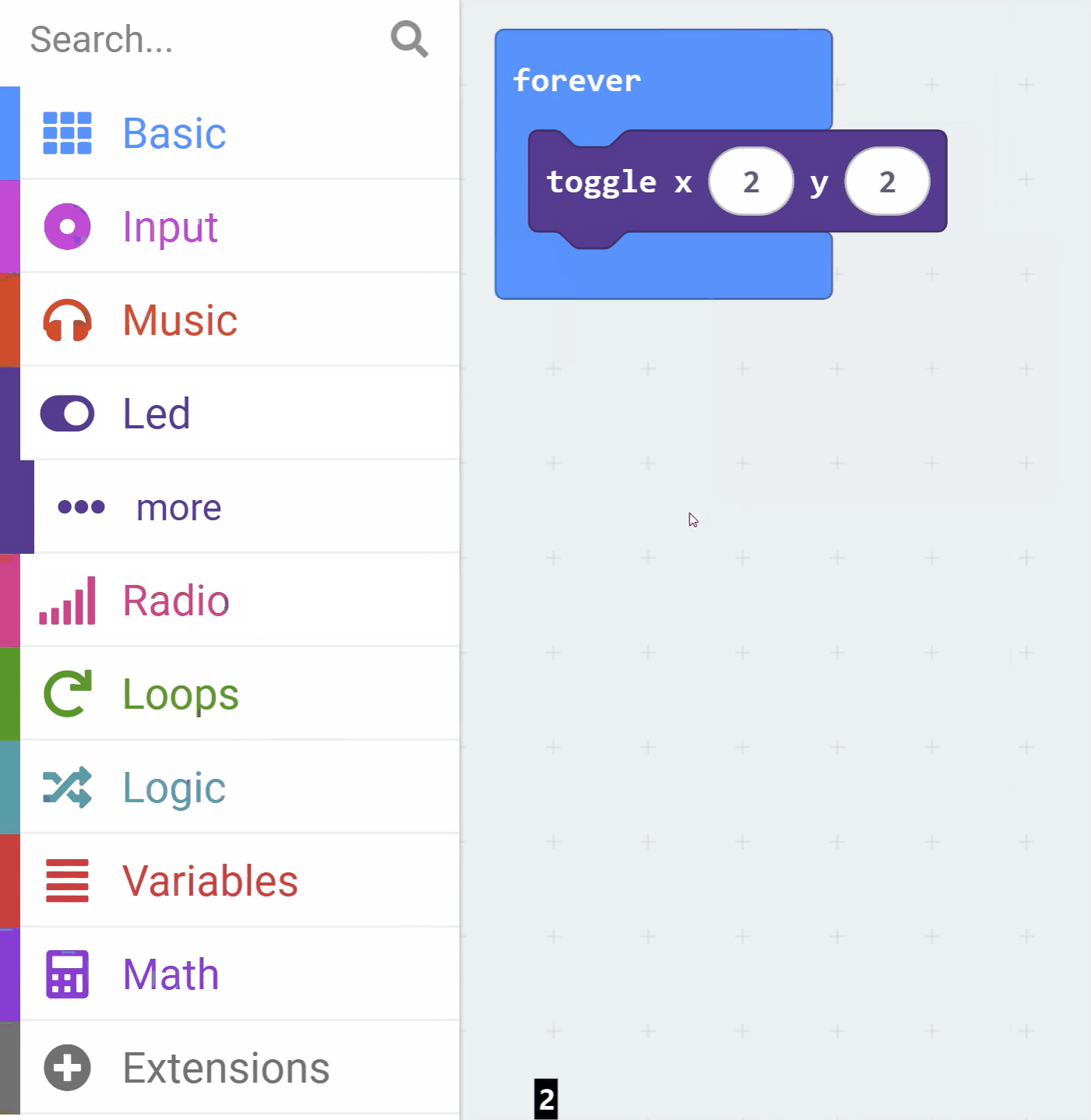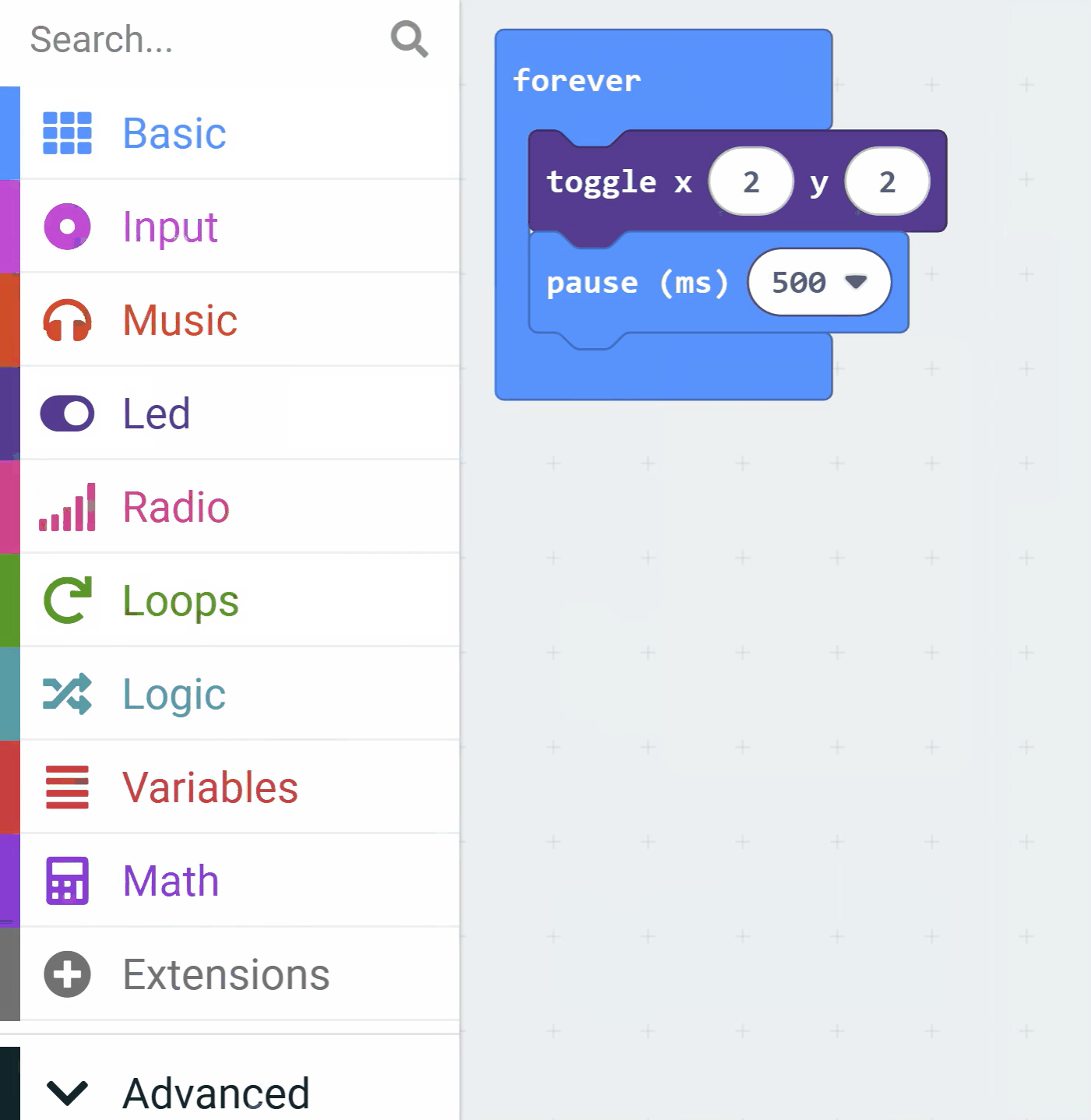
Add the following code to your project:
basic.forever(function () {
led.toggle(2, 2)
basic.pause(500)
})
Explanation of the code: The basic.forever function creates an infinite loop that runs repeatedly until the program is stopped. Inside the loop, led.toggle(2, 2) changes the state of the LED at row 2, column 2 (toggling it on or off), and basic.pause(500) waits for 500 milliseconds before the next iteration.
Once you've added the code, run it in the simulator to see the LED blink. Think about how this relates to the CPU concepts: each loop iteration represents the CPU fetching the instructions from memory, decoding what to do (toggle LED and pause), and executing those actions.