 In this lesson, you'll explore the fundamentals of algorithms, which form the backbone of computer science and programming. You'll learn how algorithms work as step-by-step instructions to solve problems, and you'll get hands-on experience visualising them through flowcharts. This will help you think logically and plan solutions effectively, skills that are crucial for coding and beyond.
In this lesson, you'll explore the fundamentals of algorithms, which form the backbone of computer science and programming. You'll learn how algorithms work as step-by-step instructions to solve problems, and you'll get hands-on experience visualising them through flowcharts. This will help you think logically and plan solutions effectively, skills that are crucial for coding and beyond.
You'll cover the following main areas:
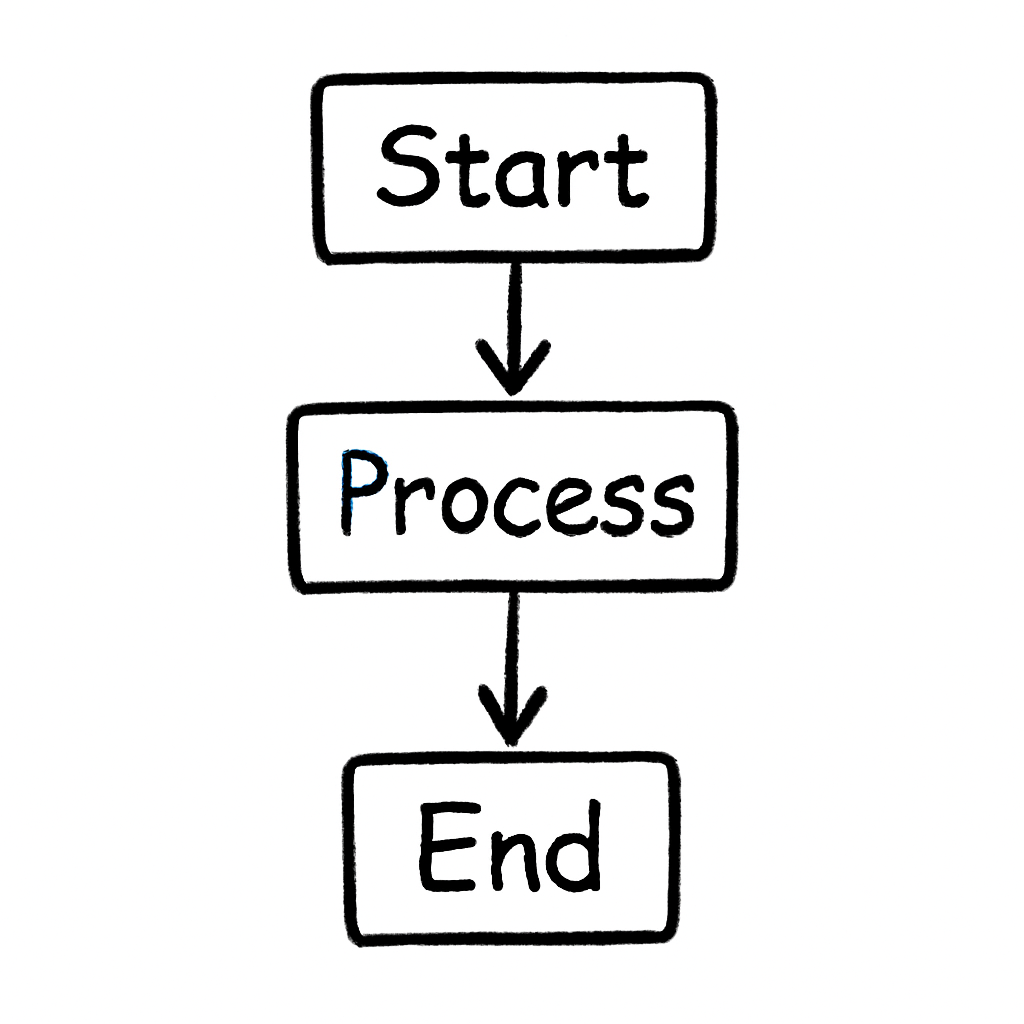 An algorithm is simply a step-by-step set of instructions that helps you solve a problem or complete a task. Imagine it as a clear guide that tells you exactly what to do, one thing at a time, in the right order, so you end up with the result you want.
An algorithm is simply a step-by-step set of instructions that helps you solve a problem or complete a task. Imagine it as a clear guide that tells you exactly what to do, one thing at a time, in the right order, so you end up with the result you want.
Think of it like following a recipe to make your favourite sandwich. The recipe might say:
If you follow these steps exactly, you get a perfect sandwich every time! That's an algorithm—it's all about breaking things down into simple, ordered steps.
Now, why is this important in computers? Computers can't think like we do; they need these precise instructions to do anything. Algorithms are the building blocks of computer science. They help computers process information, make choices, and solve problems. For example, when you search for something online, an algorithm quickly finds the best results for you. Or on social media, algorithms decide what posts show up in your feed based on what you like.
Good algorithms share certain properties that make them effective and reliable. Understanding these properties will help you design better algorithms in your coding projects. Let's explore each one in detail, with examples to make them clearer.
 An algorithm must be precise, meaning every step is clear, specific, and leaves no room for confusion or different interpretations. Think of it like giving directions to a friend: if you say "turn left at the big tree," it might be ambiguous if there are multiple trees. A precise algorithm would say "turn left at the oak tree next to the green postbox."
An algorithm must be precise, meaning every step is clear, specific, and leaves no room for confusion or different interpretations. Think of it like giving directions to a friend: if you say "turn left at the big tree," it might be ambiguous if there are multiple trees. A precise algorithm would say "turn left at the oak tree next to the green postbox."
Algorithms must be finite, which means they have a clear beginning and end, and they don't go on forever. They should complete in a reasonable number of steps.
Example: An algorithm for counting to 10 starts at 1 and stops at 10. If it kept counting endlessly, it wouldn't be finite and would never finish.
An algorithm needs to be effective, solving the problem correctly and producing the right output for any valid input.
Example: A sorting algorithm should arrange a list of numbers in ascending order without errors, no matter what numbers you give it (as long as they're valid).
Finally, good algorithms are efficient, using resources like time and memory wisely. They should solve the problem as quickly as possible without wasting unnecessary steps.
Example: To find a book in a library, checking every shelf in order is precise and finite, but it's inefficient in a large library. A better algorithm might use the Dewey Decimal System to narrow it down quickly, saving time.
Remember, not all algorithms need to be perfectly efficient for simple tasks, but in computing, efficiency becomes crucial for handling large amounts of data. As you create your own algorithms, try to check if they meet these properties.
Flowcharts are a fantastic way to visualise algorithms. They use simple shapes and arrows to represent the steps in a process, making it easier to plan, understand, and debug your ideas before you start coding. Think of a flowchart as a map that guides you through the logic of an algorithm, showing how decisions lead to different paths.
Flowcharts help break down complex problems into manageable steps. They are especially useful in programming because they allow you to spot errors or inefficiencies early on. For example, if you're designing a game or an app, a flowchart can outline the user choices and outcomes without writing a single line of code.
Flowcharts use standard shapes to represent different types of actions. Here's a quick guide to the most common ones:
Used for the start and end of the algorithm. It marks where the process begins and finishes.
Represents a process or action step, like "Display a message" or "Calculate a sum".

Indicates a decision point, where the flow branches based on a yes/no question, such as "Is it raining?".

Often used for input or output, like reading data from a user or showing results.

Shows the direction of the flow, connecting the shapes in the correct order.
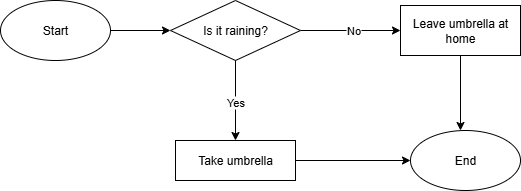
Let's create a flowchart for a basic algorithm that decides whether to take an umbrella based on the weather.
Now it's your turn to practice what you've learned about flowcharts. For this task, you'll create your own flowchart using just a pen and paper. This will help you understand how to break down a simple everyday task into an algorithm and visualise it with the shapes we've discussed.
Choose a simple task from your daily life, such as 'making a sandwich' (like the example in the first step), 'getting ready for school', or 'checking if you need an umbrella'. If you're stuck, use the sandwich example.
Follow these steps to create your flowchart:
Make it your own by adding details or changing steps to fit how you would do the task.