1 - Introduction
 Why Learn to Spot AI Online?
Why Learn to Spot AI Online?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools are capable of generating highly convincing text, images, audio, and video content. This capability is exciting as it enhances creativity and innovation. However, it also presents challenges, as it becomes increasingly important to identify AI-generated or manipulated material to avoid being misled or deceived.
In this lesson, you will explore techniques to detect AI content online, helping you become a more discerning digital citizen.
Lesson Goals
- Recognise common clues, such as artifacts, wording patterns, and inconsistencies, across various media types.
- Apply simple verification methods, including reverse image searches, source checks, and basic metadata examination.
- Develop a personal “trust checklist” that you can quickly use whenever you encounter suspicious content.
2 - Fast Checks First
 Building a Quick-Check Mindset
Building a Quick-Check Mindset
Before using advanced tools to detect AI-generated content, it is essential to develop a mindset for quick, human-led checks. These simple evaluations can help you assess the reliability of online material efficiently. By applying these checks regularly, you will become more skilled at identifying potential AI content without needing specialised software.
Here are some key quick checks to perform:
- Evaluate the Source: Consider who posted the content. Ask yourself: Is the account newly created, anonymous, or does it seem overly promotional? Reliable sources are often established and transparent about their identity.
- Examine Date and Context: Check if the content is old material being presented as new. Also, verify whether the caption or description accurately matches the media. Mismatches can indicate manipulation or reuse of content.
- Assess Perfection: AI-generated content frequently appears highly polished but lacks depth or specificity. Look for material that seems too perfect, with vague or generic details that do not provide concrete information.
- Perform a Cross-Check: Search for the same claim or information from a reputable news outlet or trusted website. If multiple reliable sources confirm the details, it increases the likelihood of authenticity.
3 - Spotting AI in Text
 Spotting AI-Written Text
Spotting AI-Written Text
Artificial Intelligence can produce text that appears well-written, but it often lacks the depth and authenticity of human writing. In this step, you will learn to identify common indicators of AI-generated text. By recognising these signs, you can better evaluate the reliability of online content.
Here are some formal indicators to look for:
- High smoothness with low specificity: The language may sound impressive and fluent, but it often avoids concrete details, reliable sources, or references to personal experiences.
- Repetitive structure: Sentences may follow similar patterns, such as consistent lengths or repeated transitional phrases like furthermore or additionally.
- Hedging and over-balancing: Phrases such as “on the one hand… on the other hand…” are common, often without committing to a clear position or conclusion.
- Generic citations: References to “experts” or “studies” without specific names, dates, or links to verifiable sources.
- Overly formal or neutral tone: The text may maintain a detached, balanced perspective that feels artificial, lacking emotional nuance or unique viewpoints.
Examples: Which Paragraph is More Likely AI-Generated?
Examine the following pairs of paragraphs and consider the indicators listed above.
Example 1
Paragraph A: “On Friday, coach Maeve O’Connor confirmed that striker Ella Byrne will miss two weeks due to an ankle sprain sustained during training. Physio Samir Patel stated that rehabilitation begins on Monday, and the team is scheduled to face Kilkenny on 12 May.”
Paragraph B: “Sports injuries represent significant concerns for teams across the globe. Athletes frequently encounter various challenges, and the recovery process encompasses numerous essential steps. Through appropriate care, successful outcomes can nevertheless be attained.”
Example 2
Paragraph A: “In 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first person to walk on the moon during the Apollo 11 mission. He famously said, 'That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.'”
Paragraph B: “Space exploration offers numerous benefits and challenges. It pushes the boundaries of human knowledge, yet requires careful planning and resources to ensure success.”
Example 3
Paragraph A: “To bake chocolate chip cookies, preheat your oven to 180°C. Mix 200g flour, 100g sugar, 100g butter, and 150g chocolate chips. Bake for 12 minutes until golden.”
Paragraph B: “Baking is a wonderful way to create delicious treats. It involves combining ingredients in harmonious ways, leading to enjoyable results for all involved.”
Example 1 - Likely AI-Generated: Paragraph B – It is vague, general, and lacks any specific sources or details. In contrast, Paragraph A includes verifiable specifics such as names, dates, and events, which are typical of human-authored content.
Example 2 - Likely AI-Generated: Paragraph B – It uses generic language and hedging without specific facts. Paragraph A has concrete historical details.
Example 3 - Likely AI-Generated: Paragraph B – It is overly general and neutral, avoiding step-by-step details. Paragraph A provides a specific recipe with measurements.
4 - Spotting AI in Images
 Can You Tell What’s Real?
Can You Tell What’s Real?
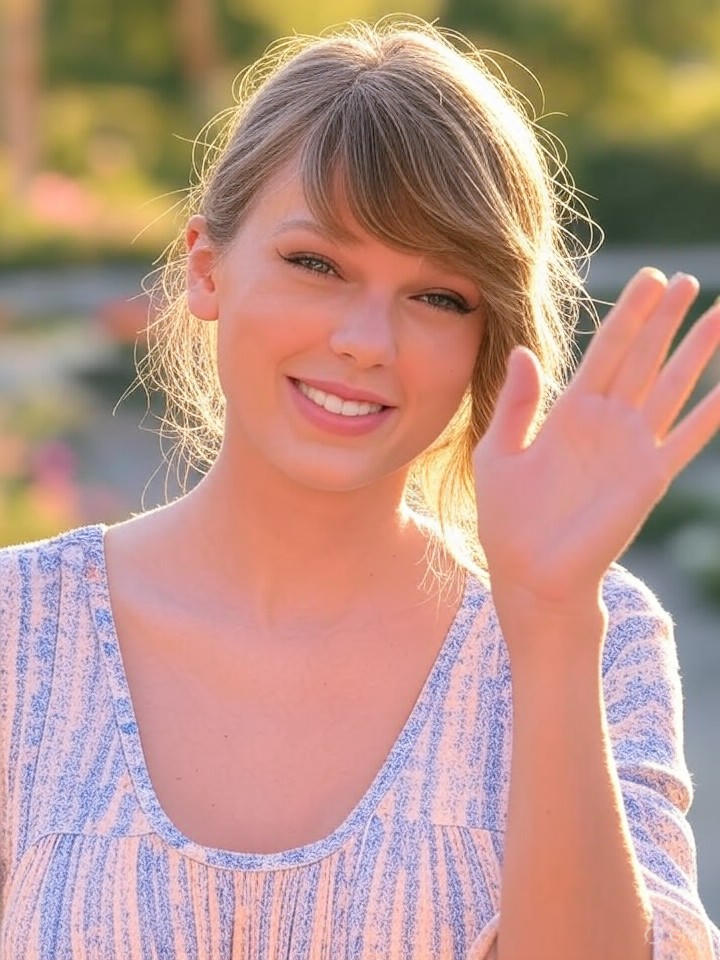
Artificial intelligence can now create incredibly realistic photos of people who don’t even exist. In this step, you’ll analyse an AI-generated image of Taylor Swift and learn how to spot the subtle details that give it away as fake.
At first glance, this picture looks like a normal photograph of Taylor Swift smiling and waving in the sunlight. But it was actually generated entirely by AI — no camera or real person was involved.
Take a closer look at the image of Taylor. Notice how some parts seem slightly off, even though it looks convincing overall.
Common Signs of AI Generation (based on this image)
- Backwards thumb: Look closely at her raised hand — the thumb appears to be positioned unnaturally, bending the wrong way. AI image models often struggle with hand anatomy.
- No shadows on her neck: Despite sunlight clearly shining through her hair, there are no realistic shadows on her neck or shoulders. Real lighting would cast soft, uneven shadows here.
- Overly smooth skin: Her face and skin look airbrushed, almost too perfect. There are no pores, fine lines, or natural texture — a common giveaway of AI-generated portraits.
- Uniform lighting: The lighting appears perfectly even across her face and background, but in real outdoor photos, sunlight usually creates stronger contrasts and depth.
- Background blur and blending: The background blends too smoothly with her outline, lacking the subtle focus variation you’d expect from a camera lens.
5 - Reverse Image Search
 Verify with Reverse Image Search
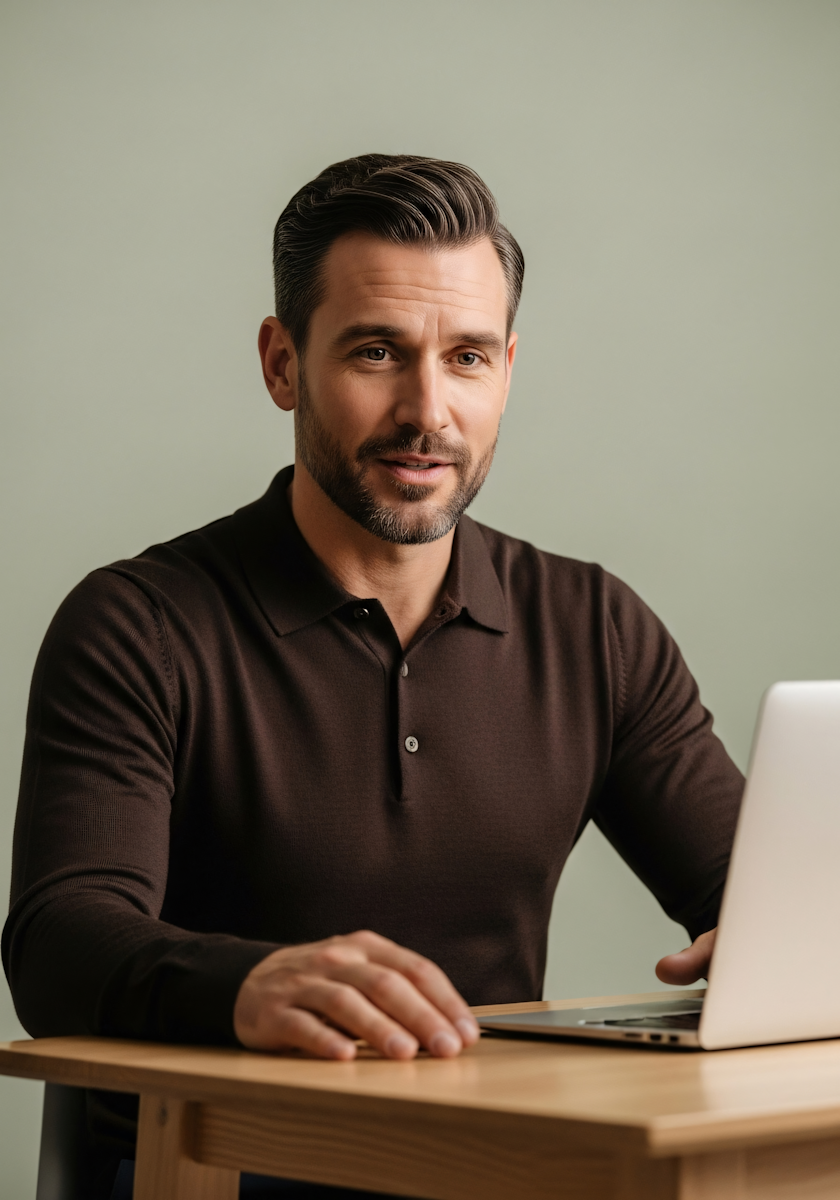
Verify with Reverse Image Search
Sometimes, AI-generated photos look completely real — like this AI-created image of a man sitting at a desk with a laptop. At first glance, nothing seems unusual, but a closer inspection reveals subtle issues, such as slightly uneven hand proportions and unnatural lighting on his face and hand.
This is where reverse image search becomes incredibly useful. It helps you verify whether an image is genuine, AI-generated, or has been used out of context. Use search tools to trace where an image has appeared before and what context it was originally used in.
- Open a reverse image tool such as Google Images or Bing Visual Search.
- Upload or paste the image URL — for example, this photo of the man at the desk.
Right Click > Copy Image Address - Review the results to find:
- The earliest upload date or appearance online.
- Trusted websites that have published the image.
- Different versions or captions that may reveal manipulation.
- Compare cropped sections (like just the face or background) to uncover hidden edits or reused AI elements.
This lesson is copyright of DigitalSkills.org 2017 - 2025. Unauthorised use, copying or distribution is not allowed.