 In this lesson, you'll learn how to handle GET and POST requests in Flask, which are essential for building interactive web applications.
In this lesson, you'll learn how to handle GET and POST requests in Flask, which are essential for building interactive web applications.
GET requests are used to retrieve data, while POST requests are used to send data to the server, like submitting a form. You'll build on your knowledge from previous Flask lessons by creating an app that manages both types of requests. Here's what you'll do:
By the end, you'll understand how to manage user inputs and responses in a web backend.
To begin, create a dedicated folder for this lesson's project to keep everything organised.
FlaskRequests'. You can place it in your Documents folder or any preferred location.File > Open Folder, then select the 'FlaskRequests' folder.With your project folder ready, you're set to create a terminal in the next step.
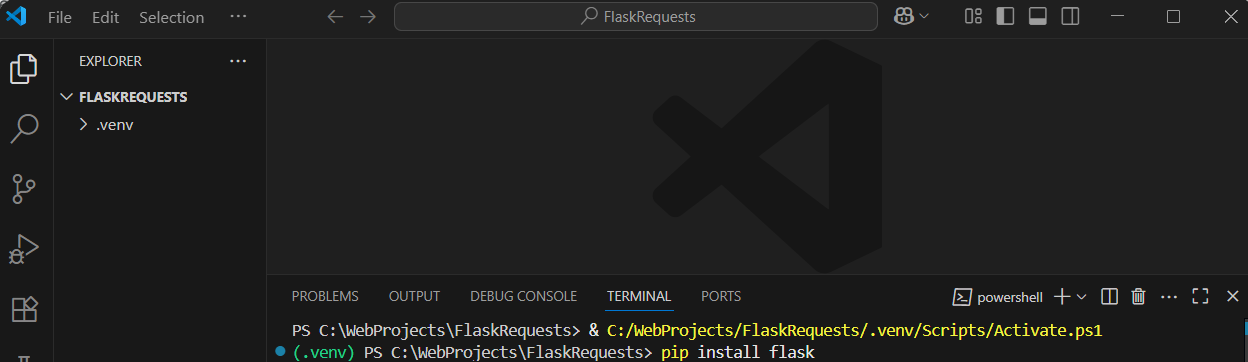
Create a virtual environment to manage your project's dependencies separately.
View > Command Palette.Python: Create Environment' and select it.Venv' as the type.Python version..venv' folder in 'FlaskRequests'.Now, open a terminal in VS Code to install Flask if it's not already installed.
View > Terminalpip install flaskLet's create a simple Flask app that handles a GET request.
GET requests are the most common type of HTTP request. They are used to retrieve data from a server without changing anything on the server. For example, when you visit a website in your browser, you're usually making a GET request to fetch the page content. In Flask, we use GET requests to display information or forms to the user.
In VS Code, create a file named 'app.py' in 'FlaskRequests'.
Add the following code:
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def home():
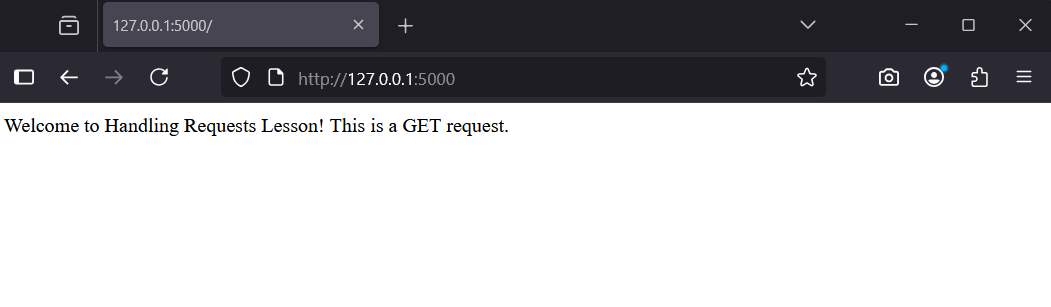
return 'Welcome to Handling Requests Lesson! This is a GET request.'Save the file.
Run python -m flask run in the terminal.
Visit http://127.0.0.1:5000/ in your browser to see the message.
Stop the server with Ctrl+C.
.png)