In this lesson, you'll dive into Flask, a lightweight Python framework for building web applications. You'll gain practical skills in web development by setting up your environment and creating a simple app from scratch. Here's what you'll be learning and doing:
By the end, you'll have a solid foundation in Flask and be ready to develop more complex web projects.
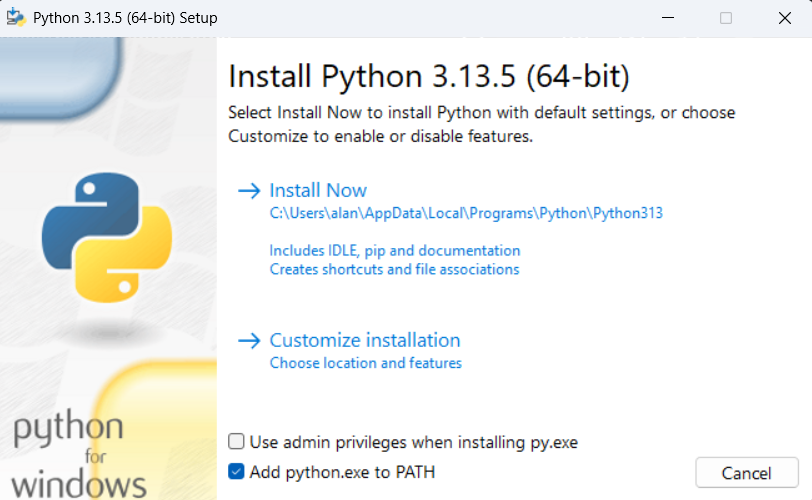
First, you need to ensure Python is installed on your computer. If you already have Python installed, you can skip to the next step. Otherwise, follow these instructions:
python --version to verify it's installed correctly. You should see the Python version number.This setup ensures you can run Python code on your machine.
If you're on Windows and running python --version opens the Microsoft Store, or shows a message like "Python was not found; run without arguments to install from the Microsoft Store, or disable this shortcut from Settings > Apps > Advanced app settings > App execution aliases.", instead of showing the version, this is due to the Microsoft Store alias interfering. To disable it:
python --version again in the command prompt.Now that Python is installed, let's set up Visual Studio Code (VS Code) to work with Python. If you don't have VS Code installed, download it from the official website: VS Code Download.
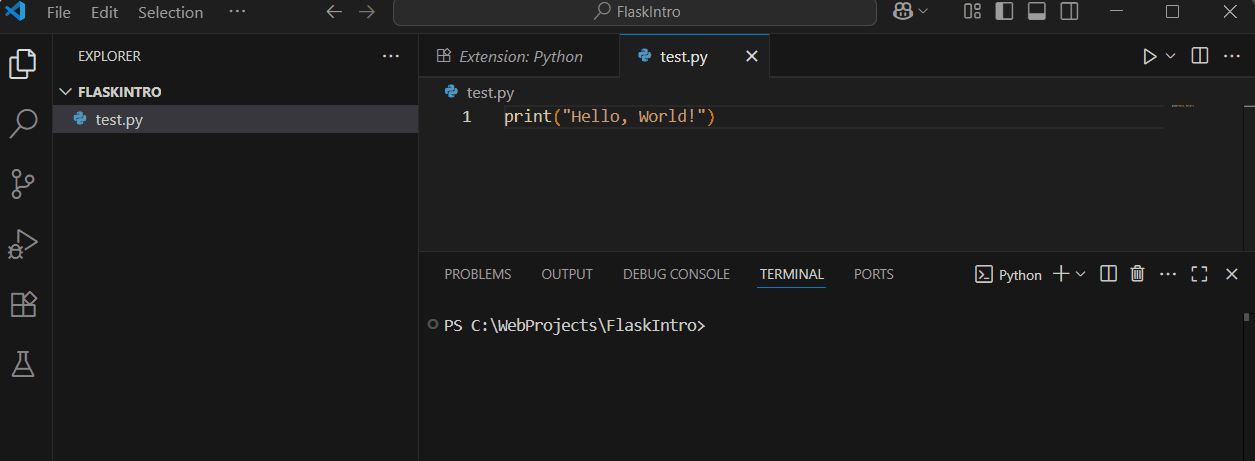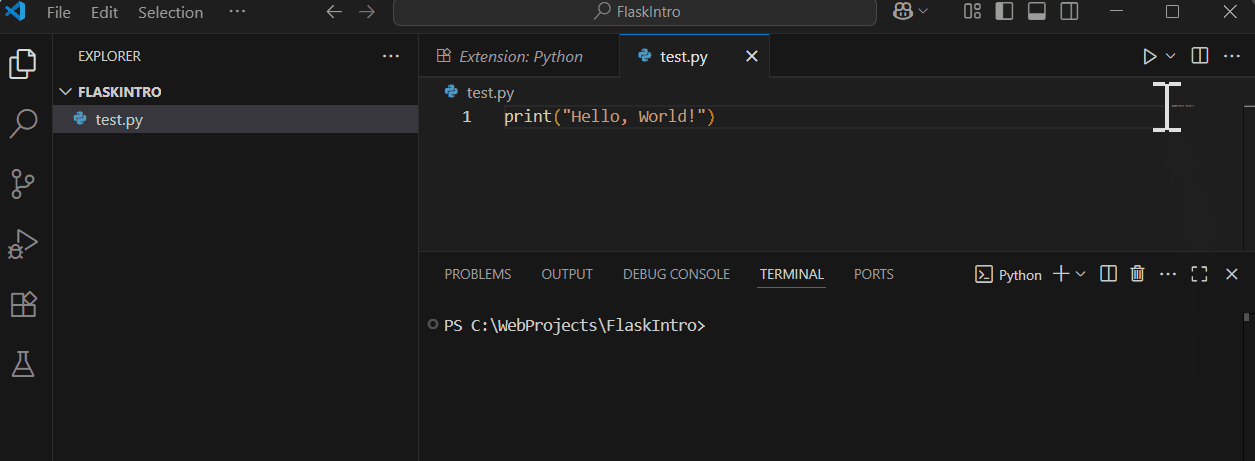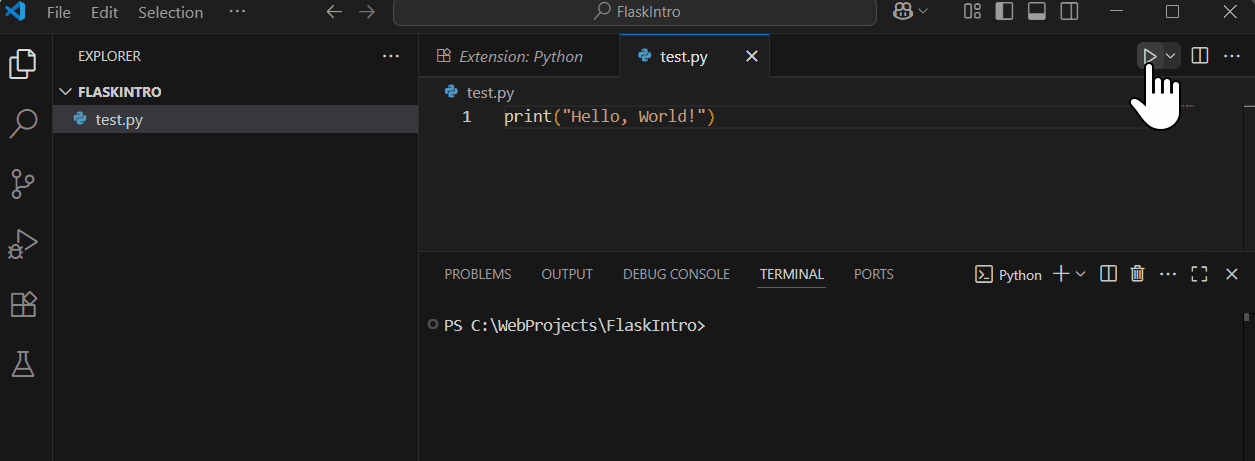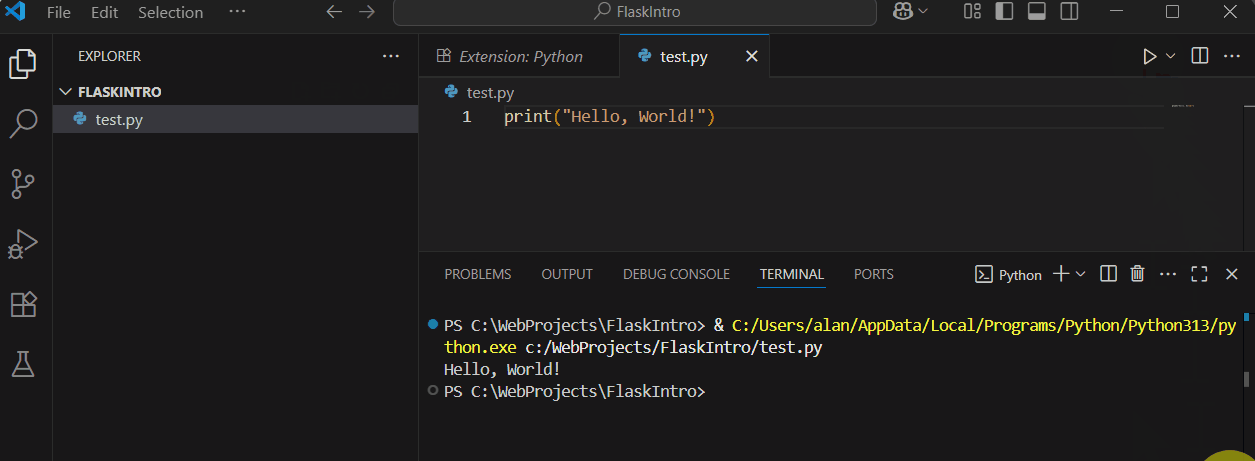
To test, create a new file named 'test.py', type print("Hello, World!"), save it, and run it by right-clicking in the editor and selecting 'Run Python File in Terminal'. You should see 'Hello, World!' in the terminal.
This prepares VS Code as your coding environment for Python projects.
Before we start building our Flask application, you need to create a dedicated folder for your project. This will help keep everything organised.
FlaskIntro'. You can do this in your Documents folder or any location you prefer.File > Open Folder and select the 'FlaskIntro' folder you just created.FlaskIntro' as your workspace, where you'll add files and code for this lesson.Before installing Flask, it's good practice to create a virtual environment. A virtual environment is like a separate, isolated space on your computer for your Python project. It allows you to install and manage packages (such as libraries) specifically for this project without interfering with other Python projects or the main Python installation on your machine. This helps avoid version conflicts and keeps things organised.
Project dependencies are the external packages or libraries that your code relies on to work properly. For example, in this lesson, Flask is a dependency because your web app needs it to run.
With your 'FlaskIntro' folder open in VS Code:
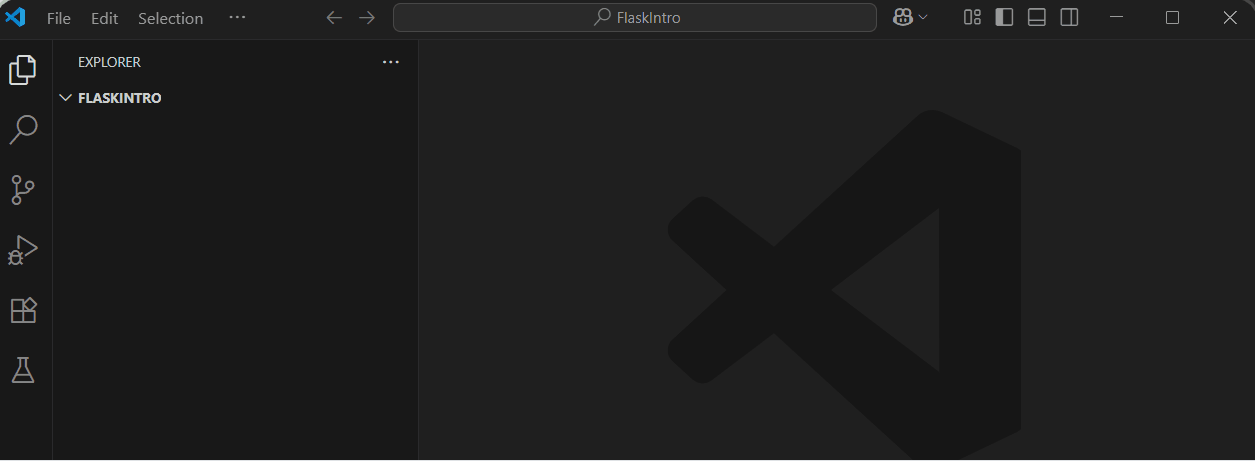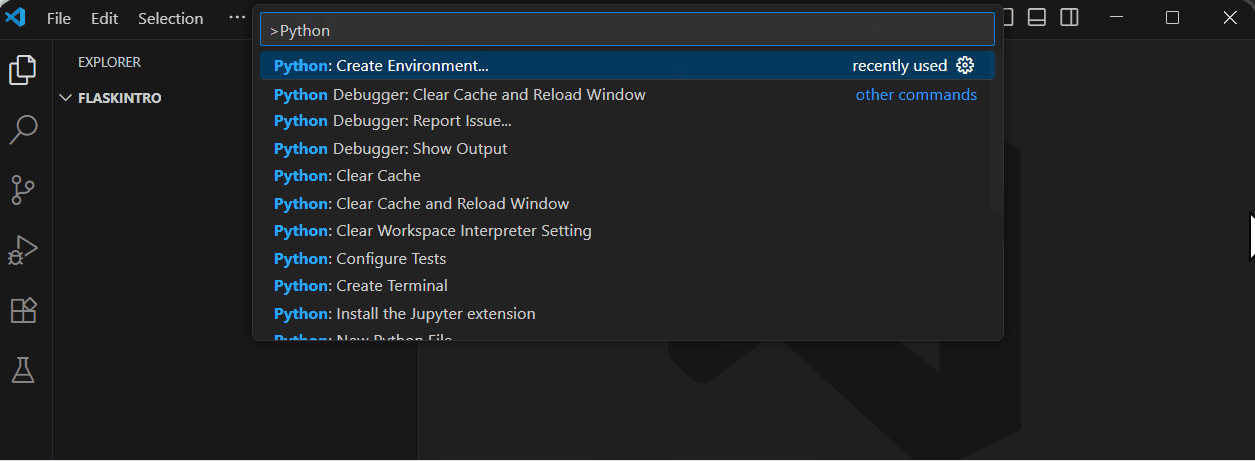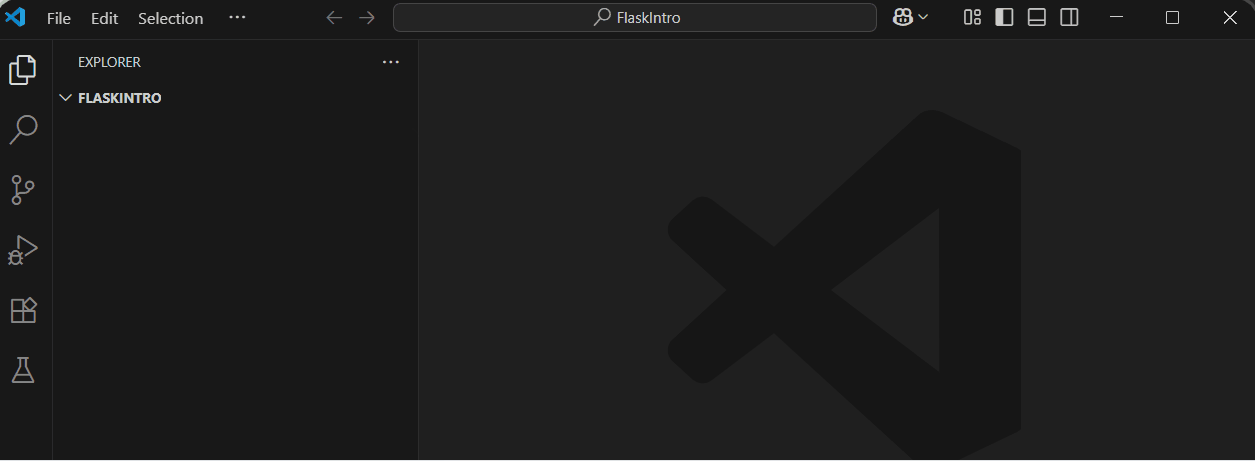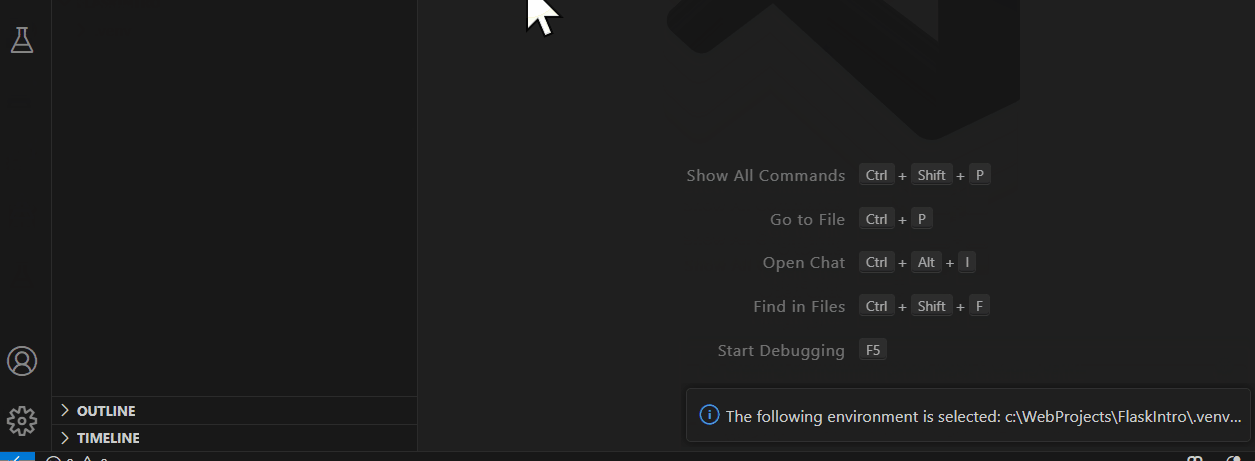
View > Command Palette.Python: Create Environment' and select it from the list.Venv' as the environment type (this creates a standard virtual environment).Python version as the interpreter..venv' in your 'FlaskIntro' directory. This may take a moment.