In this lesson, you will learn about error handling and debugging in Python web development. Understanding how to manage errors and fix bugs is crucial for building reliable applications. You will create a simple Flask app that interacts with a database, intentionally introduce errors, and learn how to handle and debug them.
In this lesson, you will learn about error handling and debugging in Python web development. Understanding how to manage errors and fix bugs is crucial for building reliable applications. You will create a simple Flask app that interacts with a database, intentionally introduce errors, and learn how to handle and debug them.
By the end, you will know how to use try-except blocks for error handling, debug code in VS Code, and avoid common pitfalls like incorrect database connections or unhandled exceptions.
First, you need to create a new folder for this lesson's project and set up the environment.
FlaskErrorHandling'.File > Open Folder).Next, create a virtual environment to manage your project's dependencies.
View > Command Palette.Python: Create Environment' and select it.Venv'..venv' folder.Next, Open a terminal in VS Code to install Flask.
View > Terminal.pip install flask.You will create a sample SQLite database with a 'users' table. This will be used in your Flask app.
Create a new file called 'create_db.py' in your project folder and add the following code:
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('users.db')
c = conn.cursor()
c.execute('''CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users
(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
age INTEGER NOT NULL)''')
# Insert sample data
c.execute("INSERT INTO users (name, age) VALUES ('Alice', 25)")
c.execute("INSERT INTO users (name, age) VALUES ('Bob', 30)")
conn.commit()
conn.close()
print('Database created successfully!')Run this script in the terminal: python create_db.py.
You should see 'Database created successfully!' and a new file 'users.db' in your folder. This database has a users table with two sample records.
Now, create a basic Flask app to display users from the database. This will be the foundation where we introduce errors.
Create a file called 'app.py' and add the following code:
from flask import Flask, render_template
import sqlite3
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def home():
conn = sqlite3.connect('users.db')
c = conn.cursor()
c.execute("SELECT * FROM users")
users = c.fetchall()
conn.close()
return render_template('users.html', users=users)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)Create a 'templates' folder and then create the 'users.html' in it with:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>Users</title></head>
<body>
<h1>Users</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr><th>ID</th><th>Name</th><th>Age</th></tr>
{% for user in users %}
<tr><td>{{ user[0] }}</td><td>{{ user[1] }}</td><td>{{ user[2] }}</td></tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</body>
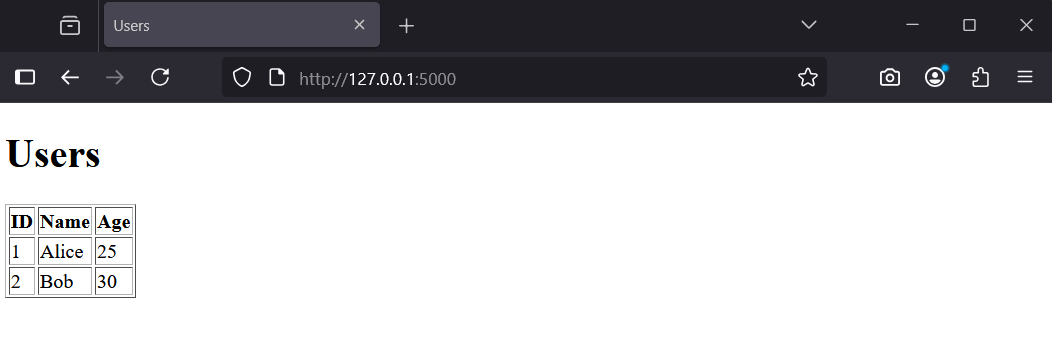
</html>Run the app: python app.py. Visit http://127.0.0.1:5000/ to see the users list.
You should see a table with Alice and Bob. Next, we will introduce an error.
 In programming, errors (often called bugs) are problems in your code that stop it from working as expected. They can cause your program to crash, produce wrong results, or behave unexpectedly. Understanding errors is the first step to fixing them and making your apps reliable.
In programming, errors (often called bugs) are problems in your code that stop it from working as expected. They can cause your program to crash, produce wrong results, or behave unexpectedly. Understanding errors is the first step to fixing them and making your apps reliable.
There are three main types of errors you might encounter in Python:
In this lesson on error handling and debugging for Flask web development, we'll focus on runtime errors, especially those related to databases, and how to handle them using tools like try-except blocks.
Remember, everyone makes errors – even experienced developers! The key is learning how to find and fix them.