 In this lesson, you will explore the differences between digital and analogue inputs in computing. These concepts are important for understanding how computers interact with the real world through sensors and devices.
In this lesson, you will explore the differences between digital and analogue inputs in computing. These concepts are important for understanding how computers interact with the real world through sensors and devices.
By the end of this lesson, you will:
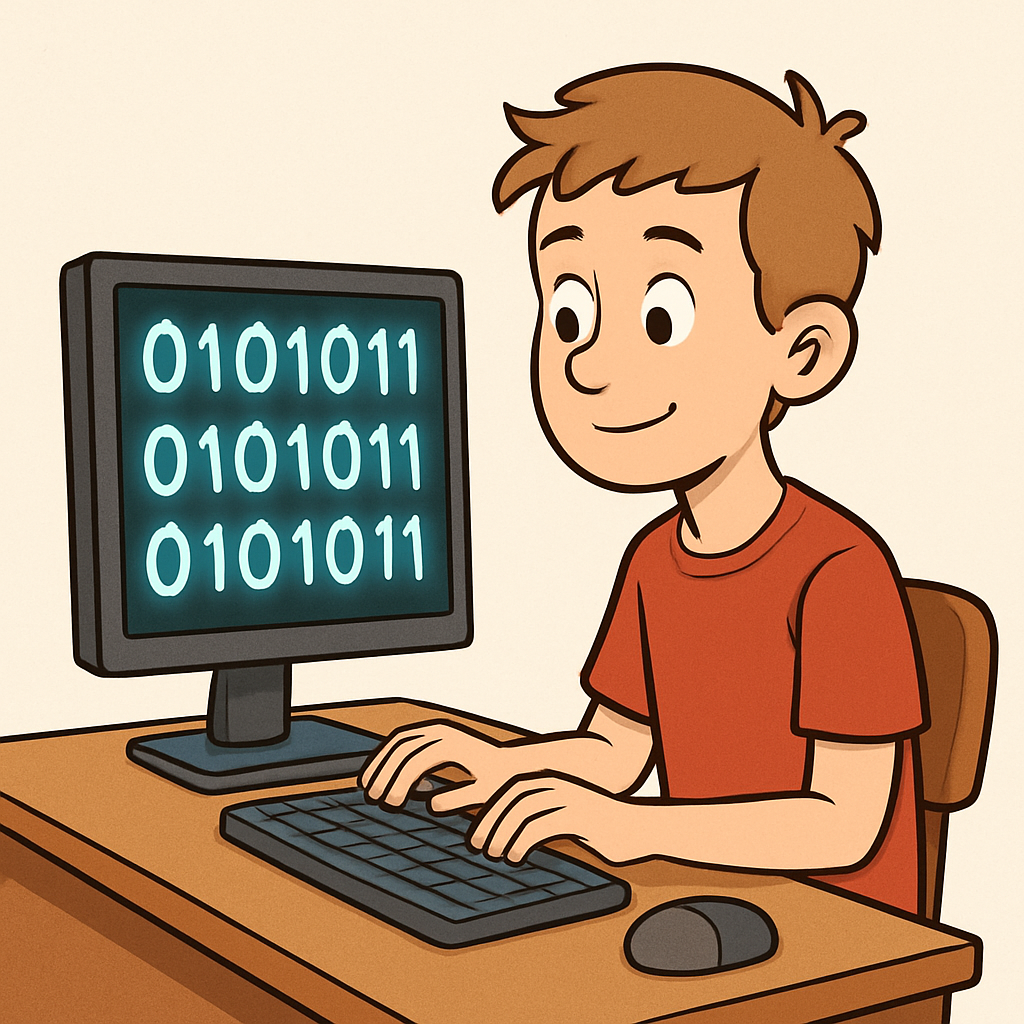 Digital input refers to data that is received in discrete, distinct values, typically represented as binary states: on or off, 0 or 1, true or false. The term 'digital' comes from 'digits,' reflecting how information is handled in countable, separate units, much like fingers on a hand. Computers process digital inputs directly because they operate in binary, which is the fundamental language of all digital devices.
Digital input refers to data that is received in discrete, distinct values, typically represented as binary states: on or off, 0 or 1, true or false. The term 'digital' comes from 'digits,' reflecting how information is handled in countable, separate units, much like fingers on a hand. Computers process digital inputs directly because they operate in binary, which is the fundamental language of all digital devices.
For example, a button press on a keyboard is a digital input – it's either pressed (1) or not pressed (0). There are no in-between states; it's all or nothing. Another common example is a light switch in your home: it's either on or off, without any gradual levels in between.
Think about how this works in everyday technology – when you press a key on your phone's screen, it's a digital input that tells the device to perform a specific action immediately.
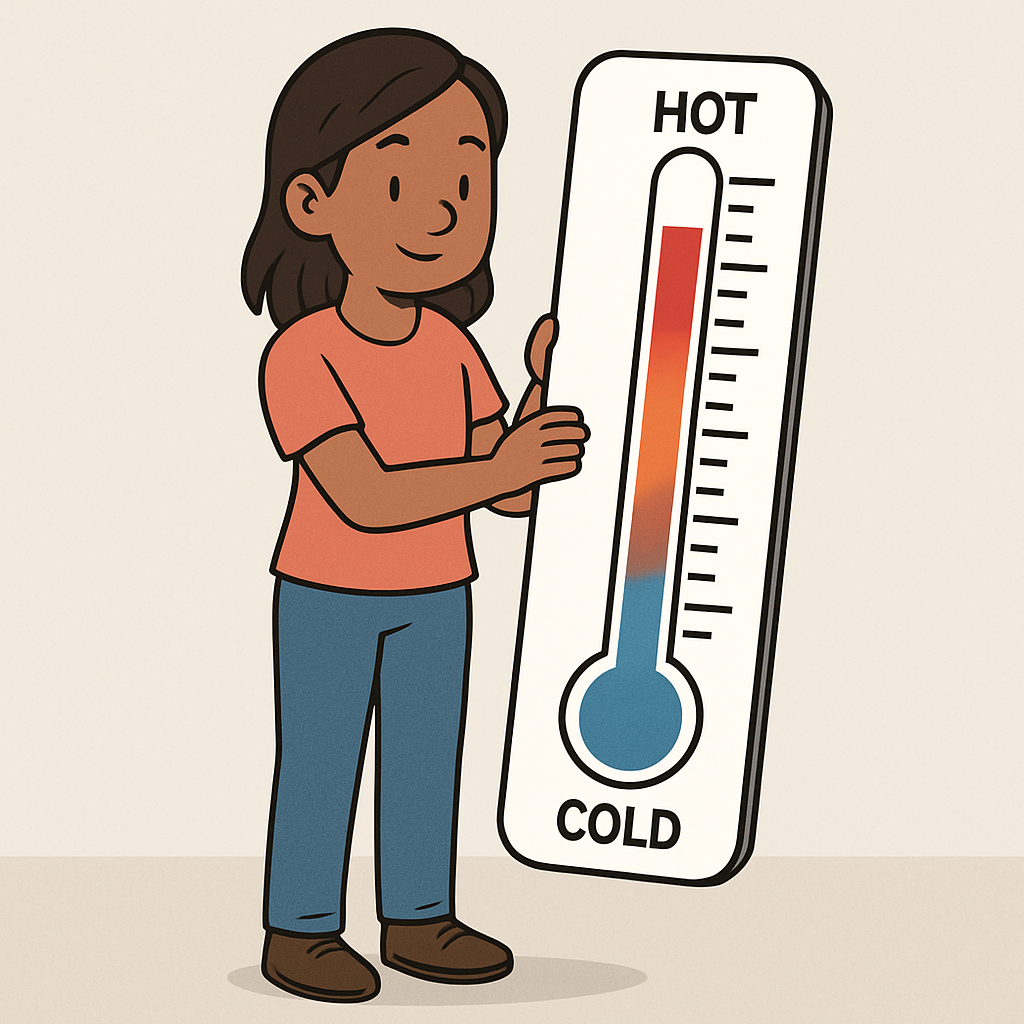 Analogue input refers to data that is continuous and can take on a range of values, not just discrete states. It represents real-world phenomena that vary smoothly, like temperature or sound levels. Unlike digital inputs, which are like simple yes/no switches, analogue inputs capture the subtle changes and variations in the environment.
Analogue input refers to data that is continuous and can take on a range of values, not just discrete states. It represents real-world phenomena that vary smoothly, like temperature or sound levels. Unlike digital inputs, which are like simple yes/no switches, analogue inputs capture the subtle changes and variations in the environment.
For instance, a thermometer measures temperature on a continuous scale, from cold to hot, with infinite possible values in between. Imagine turning a dimmer switch for a light – you can adjust it gradually to any brightness level, not just fully on or off. This is similar to how analogue inputs work, providing a smooth transition across a spectrum of values.
Another example is sound waves: when you speak, your voice creates continuous waves that vary in pitch and volume, which a microphone captures as analogue input.
Here are the main differences between digital and analogue inputs:
Understanding these differences helps in designing systems, like in networking where sensors send data over the internet.
Let's look at some real-world examples to illustrate the concepts:
In computing, a smart home system might use digital inputs from door sensors (open/closed) and analogue inputs from temperature sensors (exact room temperature).